Credit Lending
Originally contributed by: Bill Britto Smart meters have made possible new services for customers, such as automated budget assistance and bill management tools, energy use notifications, and "smart pricing" and demand response programs. It is estimated that more than 50 million smart meters have been deployed as of July 2014. Utilities and customers alike are benefiting from these smart meter deployments. It is now obvious the world of utilities is changing, and companies are beginning to cater more to their customers by offering them tools to keep their energy costs lower. For example, several companies offer prepay to some of their customers who do not have bank accounts. For many of those "unbanked" customers, prepay could be the only way to sign up for a utility services. Understanding the value of prospects and the need to automate decisions to achieve higher revenue and curb losses is imperative to the utility. It is here where a decisioning solution, like PowerCurve OnDemand> can make a real difference for utility customers by providing modified decision strategies based on market dynamics, business and economic environments. Imagine what a best of class decision solution can do by identifying what matters most about consumers and business and by leveraging internal and external data assets to replace complexity with cost efficiency? Solutions like PowerCurve OnDemand deliver the power and speed-to-market to respond to changing customer demands, driving profitability and growing customer lifetime value - good for business and good for customers.

A new comarketing agreement for MainStreet Technologies’ (MST) Loan Loss Analyzer product with Experian Decision Analytics’ Baker Hill Advisor® product will provide the banking industry with a comprehensive, automated loan-management offering. The combined products provide banks greater confidence for loan management and loan-pricing calculations. Experian Decision Analytics Baker Hill Advisor product supports banks’ commercial and small-business loan operations comprehensively, from procuring new loans through collections. MST’s Loan Loss Analyzer streamlines the estimation and documentation of the Allowance for Loan and Lease Losses (ALLL), the bank’s most critical quarterly calculation. The MST product automates the most acute processes required of community bankers in managing their commercial and small-business loan portfolios. Both systems are data-driven, configurable and designed to accommodate existing bank processes. The products already effectively work together for community banks of varying asset sizes, adding efficiencies and accuracy while addressing today’s increasingly complex regulatory requirements. “Experian’s Baker Hill Advisor product-development priorities have always been driven by our user community. Changes in regulatory and accounting requirements have our clients looking for a sophisticated ALLL system. Working with MainStreet, we can refer our clients to an industry-leading ALLL platform,” said John Watts, Experian Decision Analytics director of product management. “The sharing of data between our organizations creates an environment where strategic ALLL calculations are more robust and tactical lending decisions can be made with more confidence. It provides clients a complete service at every point within the organization.” “Bankers, including many using our Loan Loss Analyzer, have used Experian’s Baker Hill® software to manage their commercial loan programs for more than three decades,” said Dalton T. Sirmans, CEO and MST president. “Bankers who choose to implement Experian’s Baker Hill Advisor and the MST Loan Loss Analyzer will be automating their loan management, tracking, reporting and documentation in the most comprehensive, user-friendly and feature-rich manner available.” For more information on MainStreet Technologies, please visit http://www.mainstreet-tech.com/banking For more information on Baker Hill, visit http://ex.pn/BakerHill

By: Ori Eisen This article originally appeared on WIRED. When I started 41st Parameter more than a decade ago, I had a sense of what fraud was all about. I’d spent several years dealing with fraud while at VeriSign and American Express. As I considered the problem, I realized that fraud was something that could never be fully prevented. It’s a dispiriting thing to accept that committed criminals will always find some way to get through even the toughest defenses. Dispiriting, but not defeating. The reason I chose to dedicate my life to stopping online fraud is because I saw where the money was going. Once you follow the money and you see how it is used, you can’t “un-know.” The money ends up supporting criminal activities around the globe – not used to buy grandma a gift. Over the past 10 years the nature of fraud has become more sophisticated and systematized. Gone are the days of the lone wolf hacker seeing what they could get away with. Today, those days seem almost simple. Not that I should be saying it, but fraud and the people who perpetrated it had a cavalier air about them, a bravado. It was as if they were saying, in the words of my good friend Frank Abagnale, “catch me if you can.” They learned to mimic the behaviors and clone the devices of legitimate users. This allowed them to have a field day, attacking all sorts of businesses and syphoning away their ill-gotten gains. We learned too. We learned to look hard and close at the devices that attempted to access an account. We looked at things that no one knew could be seen. We learned to recognize all of the little parameters that together represented a device. We learned to notice when even one of them was off. The days of those early fraudsters has faded. New forces are at work to perpetrate fraud on an industrial scale. Criminal enterprises have arisen. Specializations have emerged. Brute force attacks, social engineering, sophisticated malware – all these tools, and so many more – are being applied every day to cracking various security systems. The criminal underworld is awash in credentials, which are being used to create accounts, take over accounts and commit fraudulent transactions. The impact is massive. Every year, billions of dollars are lost due to cyber crime. Aside from the direct monetary losses, customer lose faith in brand and businesses, resources need to be allocated to reviewing suspect transactions and creativity and energy are squandered trying to chase down new risks and threats. To make life just a little simpler, I operate from the assumption that every account, every user name and every password has been compromised. As I said at the start, fraud isn’t something that can be prevented. By hook or by crook (and mainly by crook), fraudsters are finding cracks they can slip through; it’s bound to happen. By watching carefully, we can see when they slip up and stop them from getting away with their intended crimes. If the earliest days of fraud saw impacts on individuals, and fraud today is impacting enterprises, the future of fraud is far more sinister. We’re already seeing hints of fraud’s dark future. Stories are swirling around the recent Wall Street hack. The President and his security team were watching warily, wondering if this was the result of a state-sponsored activity. Rather than just hurting businesses or their customers, we’re on the brink (if we haven’t crossed it already) of fraud being used to destabilize economies. If that doesn’t keep you up at night I don’t know what will. Think about it: in less than a decade we have gone from fraud being an isolated irritant (not that it wasn’t a problem) to being viewed as a potential, if clandestine, weapon. The stakes are no longer the funds in an account or even the well being of a business. Today – and certainly tomorrow – the stakes will be higher. Fraudsters, terrorists really, will look for ways to nudge economies toward the abyss. Sadly, the ability of fraudsters to infiltrate legitimate accounts and networks will never be fully stifled. The options available to them are just too broad for every hole to be plugged. What we can do is recognize when they’ve made it through our defenses and prevent them from taking action. It’s the same approach we’ve always had: they may get in while we do everything possible to prevent them from doing harm. In an ideal world bad guys would never get through in the first place; but we don’t live in an ideal world. In the real world they’re going to get in. Knowing this isn’t easy. It isn’t comforting or comfortable. But in the real world there are real actions we can take to protect the things that matter – your money, your data and your sense of security. We learned how to fight fraud in the past, we are fighting it with new technologies today and we will continue to apply insights and new approaches to protect our future. Download our Perspective Paper to learn about a number of factors that are contributing to the evolving fraud landscape.

Through all the rather “invented conflict” of MCX vs Apple Pay by the tech media these last few weeks – very little diligence was done on why merchants have come to reject NFC (near field communication) as the standard of choice. Maybe I can provide some color here – both as to why traditionally merchants have viewed this channel with suspicion leading up to CurrenC choosing QR, and why I believe its time for merchants to give up hating on a radio. Why do merchants hate NFC? Traditionally, any contactless usage in stores stems from international travelers, fragmented mobile NFC rollouts and a cornucopia of failed products using a variety of form factors – all of which effectively was a contactless chip card with some plastic around it. Any merchant supported tended to be in the QSR space – biggest of which was McDonalds - and they saw little to no volume to justify the upgrade costs. Magstripe, on the other hand, was a form factor that was more accessible. It was cheap to manufacture, provisioning was a snap, distribution depended primarily on USPS. Retailers used the form factor themselves for Gift cards, Pre-paid and Private Label. In contrast – complexity varies in contactless for all three – production, provisioning and distribution. If it’s a contactless card – all three can still follow pretty much the norm – as they require no customization or changes post-production. Mobile NFC was an entirely different beast. Depending on the litany of stakeholders in the value chain – from Hardware – OEM and Chipset support – NFC Controller to the Secure Element, the OS Support for the NFC stack, the Services – Trusted Service Managers of each flavor (SE vs SP), the Carriers (in case of OTA provisioning) and the list goes on. The NFC Ecosystem truly deters new entrants by its complexity and costs. Next – there was much ambiguity to what NFC/contactless could come to represent at the point of sale. Merchants delineated an open standard that could ferry over any type of credential – both credit and debit. Even though merchants prefer debit, the true price of a debit transaction varies depending on which set of rails carry the transaction – PIN Debit vs Signature Debit. And the lack of any PIN Debit networks around the contactless paradigm made the merchants fears real – that all debit transactions through NFC will be carried over the more costly signature debit route (favoring V/MA) and that a shift from magstripe to contactless would mean the end to another cost advantage the merchants had to steer transactions towards cheaper rails. The 13 or so PIN debit networks are missing from Apple Pay – and it’s an absence that weighed heavily in the merchants decision to be suspicious of it. Maybe even more important for the merchant – since it has little to do with payment – loyalty was a component that was inadequately addressed via NFC. NFC was effective as a secure communications channel – but was wholly inadequate when it came to transferring loyalty credentials, coupons and other things that justify why merchants would invest in a new technology in the first place. The contactless standards to move non-payment information, centered around ISO 18092 – and had fragmented acceptance in the retail space, and still struggled from a rather constricted pipe. NFC was simply useful as a payments standard and when it came to loyalty – the “invented a decade ago” standard is wholly inadequate to do anything meaningful at the point of sale. If the merchant must wrestle with new ways to do loyalty – then should they go back in time to enable payments, or should they jerry rig payments to be wrapped in to loyalty? What looks better to a merchant? Sending a loyalty token along with the payment credential (via ISO 18092) OR Encapsulating a payment token (as a QR Code) inside the Starbucks Loyalty App? I would guess – the latter. Even more so because in the scenario of accepting a loyalty token alongside an NFC payment – you are trusting the payment enabler (Apple, Google, Networks, Banks) with your loyalty token. Why would you? The reverse makes sense for a merchant. Finally – traditional NFC payments – (before Host Card Emulation in Android) – apart from being needlessly complex – mandated that all communication between the NFC capable device and the point-of-sale terminal be limited to the Secure Element that hosts the credential and the payment applets. Which means if you did not pay your way in to the Secure Element (mostly only due to if you are an issuer) then you have no play. What’s a merchant to do? So if you are a merchant – you are starting off with a disadvantage – as those terminologies and relationships are alien to you. Merchants did not own the credential – unless it was prepaid or private label – and even then, the economics wouldn’t make sense to put those in a Secure Element. Further, Merchants had no control in the issuer’s choice of credential in the Secure Element – which tended to be mostly credit. It was then no surprise that merchants largely avoided this channel – and then gradually started to look at it with suspicion around the same time banks and networks began to pre-ordain NFC as the next stage in payment acceptance evolution. Retailers who by then had been legally embroiled in a number of skirmishes on the interchange front – saw this move as the next land grab. If merchants could not cost effectively compete in this new channel – then credit was most likely to become the most prevalent payment option within. This suspicion was further reinforced with the launch of GoogleWallet, ISIS and now Apple Pay. Each of these wrapped existing rails, maintained status quo and allowed issuers and networks to bridge the gap from plastic to a new modality (smartphones) while changing little else. This is no mere paranoia. The merchants fear that issuers and networks will ultimately use the security and convenience proffered through this channel as an excuse to raise rates again. Or squeeze out the cheaper alternatives – as they did with defaulting to Signature Debit over PIN debit for contactless. As consumers learn a new behavior (tap and pay) they fear that magstripe will eclipse and a high cost alternative will then take root. How is it fair that to access their customer’s funds – our money – one has to go through toll gates that are incentivized to charge higher prices? The fact that there are little to no alternatives between using Cash or using a bank issued instrument to pay for things – should worry us as consumers. As long as merchants are complacent about the costs in place for them to access our money – there won’t be much of an incentive for banks to find quicker and cheaper ways to move money – in and out of the system as a whole. I digress. So the costs and complexities that I pointed to before, that existed in the NFC payments ecosystem – served to not only keep retailers out, but also impacted issuers ability to scale NFC payments. These costs materialized in to higher interchange cards for the issuer when these initiatives took flight – partly because the issuer was losing money already, and had then little interest to enable debit as a payments choice. GoogleWallet itself had to resort to a bit of “negative margin strategy” to allow debit cards to be used within. ISIS had little to no clout, nor any interest to push issuers to pick debit. All of which must have been quite vexing for an observant merchant. Furthermore, just as digital and mobile offers newer ways to interact with consumers – they also portend a new reality – that new ecosystems are taking shape across that landscape. And these ecosystems are hardly open – Facebook, Twitter, Google, Apple – and they have their own toll gates as well. Finally – A retail payment friend told me recently that merchants view the plethora of software, systems and services that encapsulate cross-channel commerce as a form of “Retailer OS”. And if Payment acceptance devices are end-points in to that closed ecosystem of systems and software – they are rightfully hesitant in handing over those keys to the networks and banks. The last thing they want to do is let someone else control those toll-gates. And it makes sense and ironically – it has parallel in the iOS ecosystem. Apple’s MFi program is an example of an ecosystem owner choosing to secure those end-points – especially when those are manufactured by a third party. This is why Apple exacts a toll and mandates that third party iOS accessory manufacturers must include an Apple IC to securely connect and communicate with an iOS device. If Apple can mandate that, then why is it that a retailer should have no say over the end-points through which payments occur in it’s own retail ecosystem? Too late to write about how the retailer view of NFC must evolve – in the face of an open standard, aided by Host Card Emulation – but that’s gotta be another post. Another time. See you all in Vegas. Make sure to join the Experian #MobilePayChat on Twitter this Tuesday at 12:15 p.m. PT during Money2020 conference: http://ex.pn/Money2020. If you are attending the event please stop by our booth #218. This post originally appeared here.

By: John Robertson I began this blog series asking the question “How can banks offer such low rates?” Exploring the relationship of pricing in an environment where we have a normalized. I outlined a simplistic view of loan pricing as: + Interest Income + Non-Interest Income Cost of Funds Non-Interest Expense Risk Expense = Income before Tax Along those lines, I outlined how perplexing it is to think at some of these current levels, banks could possibly make any money. I suggested these offerings must be lost leaders with the anticipation of more business in the future or possibly, additional deposits to maintain a hold on the relationship over time. Or, I shudder to think, banks could be short funding the loans with the excess cash on their balance sheets. I did stumble across another possibility while proving out an old theory which was very revealing. The old theory stated by a professor many years ago was “Margins will continue to narrow…. Forever”. We’ve certainly seen that in the consumer world. In pursuit of proof to this theory I went to the trusty UBPR and looked at the net interest margin results from 2011 until today for two peer groups (insured commercial banks from $300 million to $1 billion and insured commercial banks greater the $3 billion). What I found was, in fact, margins have narrowed anywhere from 10 to 20 basis points for those two groups during that span even though non-interest expense stayed relatively flat. Not wanting to stop there, I started looking at one of the biggest players individually and found an interesting difference in their C&I portfolio. Their non-interest expense number was comparable to the others as well as their cost of funds but the swing component was non-interest income. One line item on the UPBR’s income statement is Overhead (i.e. non-interest expense) minus non-interest income (NII). This bank had a strategic advantage when pricing there loans due to their fee income generation capabilities. They are not just looking at spread but contribution as well to ensure they meet their stated goals. So why do banks hesitate to ask for a fee if a customer wants a certain rate? Someone seems to have figured it out. Your thoughts?
Experian hosted the Future of Fraud event this week in New York City where Ori Eisen and Frank Abagnale hosted clients and prospects highlighting the need for innovative fraud solutions to stay ahead the consistent threat of online fraud. After, Ori and Frank appeared on Bloomberg TV, interviewed by Trish Regan discussing how retailers can handle fraud prevention. Ori and Frank highlighted how using data is good, especially when combined with analytics as a requirement for businesses working to try and prevent fraud now and in the future. "Data is good. The only way that you deal with a lot of this cyber(crime) is through data analytics. You have to know who I am dealing with. I have to know it is you and authenticate that it is you that wants to make this transaction." Frank Abagnale on BloombergTV Charles Chung recently detailed how utilizing the data for good can protect the customer experience while providing businesses a panoramic view to ensure data security and compliance to mitigate fraud risk. Ultimately, this view helps businesses build greater consumer confidence and create a more positive customer experience which is the first, and most important, prong in the fraud balance. Learn more on how Experian is using big data.

More than 10 years ago I spoke about a trend at the time towards an underutilization of the information being managed by companies. I referred to this trend as “data skepticism.” Companies weren’t investing the time and resources needed to harvest the most valuable asset they had – data. Today the volume and variety of data is only increasing as is the necessity to successfully analyze any relevant information to unlock its significant value. Big data can mean big opportunities for businesses and consumers. Businesses get a deeper understanding of their customers’ attitudes and preferences to make every interaction with them more relevant, secure and profitable. Consumers receive greater value through more personalized services from retailers, banks and other businesses. Recently Experian North American CEO Craig Boundy wrote about that value stating, “Data is Good… Analytics Make it Great.” The good we do with big data today in handling threats posed by fraudsters is the result of a risk-based approach that prevents fraud by combining data and analytics. Within Experian Decision Analytics our data decisioning capabilities unlock that value to ultimately provide better products and services for consumers. The same expertise, accurate and broad-reaching data assets, targeted analytics, knowledge-based authentication, and predictive decisioning policies used by our clients for risk-based decisioning has been used by Experian to become a global leader in fraud and identity solutions. The industrialization of fraud continues to grow with an estimated 10,000 fraud rings in the U.S. alone and more than 2 billion unique records exposed as a result of data breaches in 2014. Experian continues to bring together new fraud platforms to help the industry better manage fraud risk. Our 41st Parameter technology has been able to detect over 90% of all fraud attacks against our clients and reduce their operational costs to fight fraud. Combining data and analytics assets can detect fraud, but more importantly, it can also detect the good customers so legitimate transactions are not blocked. Gartner reported that by 2020, 40% of enterprises will be storing information from security events to analyze and uncover unusual patterns. Big data uncovers remarkable insights to take action for the future of our fraud prevention efforts but also can mitigate the financial losses associated with a breach. In the end we need more data, not less, to keep up with fraudsters. Experian is hosting Future of Fraud and Identity events in New York and San Francisco discussing current fraud trends and how to prevent cyber-attacks aimed at helping the industry. The past skepticism no longer holds true as companies are realizing that data combined with advanced analytics can give them the insight they need to prevent fraud in the future. Learn more on how Experian is conquering the world of big data.
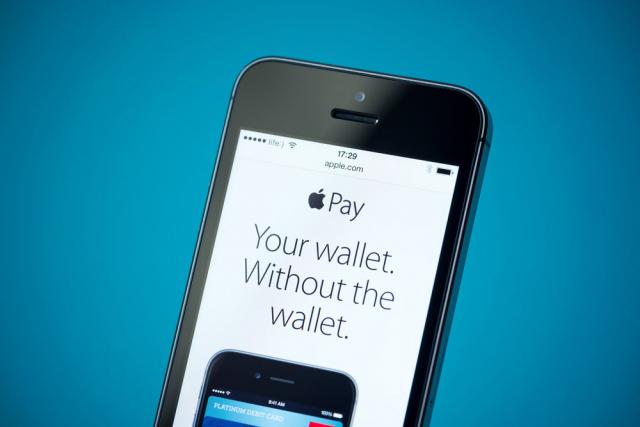
If rumors hold true, Apple Pay will launch in a week. Five of my last six posts had covered Apple’s likely and actual strategy in payments & commerce, and the rich tapestry of control, convenience, user experience, security and applied cryptography that constitutes as the backdrop. What follows is a summation of my views – with a couple of observations from having seen the Apple Pay payment experience up close. About three years ago – I published a similar commentary on Google Wallet that for kicks, you can find here. I hope what follows is a balanced perspective, as I try to cut through some FUD, provide some commentary on the payment experience, and offer up some predictions that are worth the price you pay to read my blog. Source: Bloomua / Shutterstock.com First the criticism. Apple Pay doesn’t go far enough: Fair. But you seem to misunderstand Apple’s intentions here. Apple did not set out to make a mobile wallet. Apple Pay sits within Passbook – which in itself is a wrapper of rewards and loyalty cards issued by third parties. Similarly – Apple Pay is a wrapper of payments cards issued by third parties. Even the branding disappears once you provision your cards – when you are at the point-of-sale and your iPhone6 is in proximity to the reader (or enters the magnetic field created by the reader) – the screen turns on and your default payment card is displayed. One does not need to launch an app or fiddle around with Apple Pay. And for that matter, it’s even more limited than you think. Apple’s choice to leave the Passbook driven Apple Pay experience as threadbare as possible seems an intentional choice to force consumers to interact more with their bank apps vs Passbook for all and any rich interaction. Infact the transaction detail displayed on the back of the payment card you use is limited – but you can launch the bank app to view and do a lot more. Similarly – the bank app can prompt a transaction alert that the consumer can select to view more detail as well. Counter to what has been publicized – Apple can – if they choose to – view transaction detail including consumer info, but only retains anonymized info on their servers. The contrast is apparent with Google – where (during early Google Wallet days) issuers dangled the same anonymized transaction info to appease Google – in return for participation in the wallet. If your tap don’t work – will you blame Apple? Some claim that any transaction failures – such as a non-working reader – will cause consumers to blame Apple. This does not hold water simply because – Apple does not get in between the consumer, his chosen card and the merchant during payment. It provides the framework to trigger and communicate a payment credential – and then quietly gets out of the way. This is where Google stumbled – by wanting to become the perennial fly on the wall. And so if for whatever reason the transaction fails, the consumer sees no Apple branding for them to direct their blame. (I draw a contrast later on below with Samsung and LoopPay) Apple Pay is not secure: Laughable and pure FUD. This article references an UBS note talking how Apple Pay is insecure compared to – a pure cloud based solution such as the yet-to-be-launched MCX. This is due to a total misunderstanding of not just Apple Pay – but the hardware/software platform it sits within (and I am not just talking about the benefits of a TouchID, Network Tokenization, Issuer Cryptogram, Secure Element based approach) including, the full weight of security measures that has been baked in to iOS and the underlying hardware that comes together to offer the best container for payments. And against all that backdrop of applied cryptography, Apple still sought to overlay its payments approach over an existing framework. So that, when it comes to risk – it leans away from the consumer and towards a bank that understands how to manage risk. That’s the biggest disparity between these two approaches – Apple Pay and MCX – that, Apple built a secure wrapper around an existing payments hierarchy and the latter seeks to disrupt that status quo. Let the games begin: Consumers should get ready for an ad blitz from each of the launch partners of Apple Pay over the next few weeks. I expect we will also see these efforts concentrated around pockets of activation – because setting up Apple Pay is the next step to entering your Apple ID during activation. And for that reason – each of those launch partners understand the importance of reminding consumers why their card should be top of mind. There is also a subtle but important difference between top of wallet card (or default card) for payment in Apple Pay and it’s predecessors (Google Wallet for example). Changing your default card was an easy task – and wholly encapsulated – within the Google Wallet app. Where as in Apple Pay – changing your default card – is buried under Settings, and I doubt once you choose your default card – you are more likely to not bother with it. And here’s how quick the payment interaction is within Apple Pay (takes under 3 seconds) :- Bring your phone in to proximity of the reader. Screen turns on. Passbook is triggered and your default card is displayed. You place your finger and authenticate using TouchID. A beep notes the transaction is completed. You can flip the card to view a limited transaction detail. Yes – you could swipe down and choose another card to pay. But unlikely. I remember how LevelUp used very much the same strategy to signup banks – stating that over 90% of it’s customers never change their default card inside LevelUp. This will be a blatant land grab over the next few months – as tens of millions of new iPhones are activated. According to what Apple has told it’s launch partners – they do expect over 95% of activations to add at least one card. What does this mean to banks who won’t be ready in 2014 or haven’t yet signed up? As I said before – there will be a long tail of reduced utility – as we get in to community banks and credit unions. The risk is amplified because Apple Pay is the only way to enable payments in iOS that uses Apple’s secure infrastructure – and using NFC. For those still debating whether it was a shotgun wedding, Apple’s approach had five main highlights that appealed to a Bank – Utilizing an approach that was bank friendly (and to status quo) : NFC Securing the transaction beyond the prerequisites of EMV contactless – via network tokenization & TouchID Apple’s preference to stay entirely as an enabler – facilitating a secure container infrastructure to host bank issued credentials. Compressing the stack: further shortening the payment authorization required of the consumer by removing the need for PIN entry, and not introducing any new parties in to the transaction flow that could have introduced delays, costs or complexity in the roundtrip. Clear description of costs to participate – Free is ambiguous. Free leads to much angst as to what the true cost of participation really is(Remember Google Wallet?). Banks prefer clarity here – even if it means 15bps in credit. As I wrote above, Apple opting to strictly coloring inside the lines – forces the banks to shoulder much of the responsibility in dealing with the ‘before’ and ‘after’ of payment. Most of the bank partners will be updating or activating parts of their mobile app to start interacting with Passbook/Apple Pay. Much of that interaction will use existing hooks in to Passbook – and provide richer transaction detail and context within the app. This is an area of differentiation for the future – because those banks who lack the investment, talent and commitment to build a redeeming mobile services approach will struggle to differentiate on retail footprint alone. And as smarter banks build entirely digital products for an entirely digital audience – the generic approaches will struggle and I expect at some point – that this will drive bank consolidation at the low end. On the other hand – if you are an issuer, the ‘before’ and ‘after’ of payments that you are able to control and the richer story you are able to weave, along with offline incentives – can aid in recapture. The conspicuous and continued absence of Google: So whither Android? Uniformity in payments for Android is as fragmented as the ecosystem itself. Android must now look at Apple for lessons in consistency. For example, how Apple uses the same payment credential that is stored in the Secure Element for both in-person retail transactions as well as in-app payments. It may look trivial – but when you consider that Apple came dangerously close (and justified as well) in its attempt to obtain parity between those two payment scenarios from a rate economics point of view from issuers – Android flailing around without a coherent strategy is inexcusable. I will say this again: Google Wallet requires a reboot. And word from within Google is that a reboot may not imply a singular or even a cohesive approach. Google needs to swallow its pride and look to converge the Android payments and commerce experience across channels similar to iOS. Any delay or inaction risks a growing apathy from merchants who must decide what platform is worth building or focusing for. Risk vs Reward is already skewed in favor of iOS: Even if Apple was not convincing enough in its attempt to ask for Card Present rates for its in-app transactions – it may have managed to shift liability to the issuer similar to 3DS and VBV – that in itself poses an imbalance in favor of iOS. For a retail app in iOS – there is now an incentive to utilize Apple Pay and iOS instead of all the other competing payment providers (Paypal for example, or Google Wallet) because transactional risk shifts to the issuer if my consumer authenticates via TouchID and uses a card stored in Apple Pay. I have now both an incentive to prefer iOS over Android as well as an opportunity to compress my funnel – much of my imperative to collect data during the purchase was an attempt to quantify for fraud risk – and the need for that goes out of the window if the customer chooses Apple Pay. This is huge and the repercussions go beyond Android – in to CNP fraud, CRM and loyalty. Networks, Tokens and new end-points (e.g. LoopPay): The absence of uniformity in Android has provided a window of opportunity for others – regardless of how fragmented these approaches be. Networks shall parlay the success with tokenization in Apple Pay in to Android as well, soon. Prime example being: Loop Pay. If as rumors go – Samsung goes through with baking in Loop Pay in to its flagship S6, and Visa’s investment translates in to Loop using Visa tokenization – Loop may find the ubiquity it is looking for – on both ends. I don’t necessarily see the value accrued to Samsung for launching a risky play here: specifically because of the impact of putting Loop’s circuitry within S6. Any transaction failure in this case – will be attributed to Samsung, not to Loop, or the merchant, or the bank. That’s a risky move – and I hope – a well thought out one. I have some thoughts on how the Visa tokenization approach may solve for some of the challenges that Loop Pay face on merchant EMV terminals – and I will share those later. The return of the comeback: Reliance on networks for tokenization does allay some of the challenges faced by payment wrappers like Loop, Coin etc – but they all focus on the last mile and tokenization does little more for them than kicking the can down the road and delaying the inevitable a little while more. The ones that benefit most are the networks themselves – who now has wide acceptance of their tokenization service – with themselves firmly entrenched in the middle. Even though the EMVCo tokenization standard made no assumptions regarding the role of a Token Service Provider – and in fact Issuers or 3rd parties could each pay the role sufficiently well – networks have left no room for ambiguity here. With their role as a TSP – networks have more to gain from legitimizing more end points than ever before – because these translate to more token traffic and subsequently incremental revenue – transactional and additional managed services costs (OBO – On behalf of service costs incurred by a card issuer or wallet provider). It has never been a better time to be a network. I must say – a whiplash effect for all of us – who called for their demise with the Chase-VisaNet deal. So my predictions for Apple Pay a week before its launch: We will see a substantial take-up and provisioning of cards in to Passbook over the next year. Easy in-app purchases will act as the carrot for consumers. Apple Pay will be a quick affair at the point-of-sale: When I tried it few weeks ago – it took all of 3 seconds. A comparable swipe with a PIN (which is what Apple Pay equates to) took up to 10. A dip with an EMV card took 23 seconds on a good day. I am sure this is not the last time we will be measuring things. The substantial take-up on in-app transactions will drive signups: Consumers will signup because Apple’s array of in-app partners will include the likes of Delta – and any airline that shortens the whole ticket buying experience to a simple TouchID authentication has my money. Apple Pay will cause MCX to fragment: Even though I expect the initial take up to be driven more on the in-app side vs in-store, as more merchants switch to Apple Pay for in-app, consumers will expect a consistency in that approach across those merchants. We will see some high profile desertions – driven partly due to the fact that MCX asks for absolute fealty from its constituents, and in a rapidly changing and converging commerce landscape – that’s just a tall ask. In the near-term, Android will stumble: Question is if Google can reclaim and steady its own strategy. Or will it spin off another costly experiment in chasing commerce and payments. The former will require it to be pragmatic and bring ecosystem capabilities up to par – and that’s a tall ask when you lack the capacity for vertical integration that Apple has. And from the looks of it – Samsung is all over the place at the moment. Again – not confidence inducing. ISIS/SoftCard will get squeezed out of breath: SoftCard and GSMA can’t help but insert themselves in to the Apple Pay narrative by hoping that the existence of a second NFC controller on the iPhone6 validates/favors their SIM based Secure Element approach and indirectly offers Softcard/GSMA constituents a pathway to Apple Pay. If that didn’t make a lick of sense – It’s like saying ‘I’m happy about my neighbor’s Tesla because he plugs it in to my electric socket’. Discover how an Experian business consultant can help you strengthen your credit and risk management strategies and processes: http://ex.pn/DA_GCP This post originally appeared here.

By: Joel Pruis When the OCC put forth the supervisory guidance on model risk governance the big focus in the industry was around the larger financial institutions that had created their own risk models. The overall intent to make sure that the larger financial institutions were properly managing the risk they were assuming through the use of the custom risk models they had developed. While we can’t say that this model risk governance was a significant issue, the guidance provided by the OCC is intended to provide financial institutions with the minimum requirements for model risk governance. Now that the OCC and the Federal Reserve have gone through the model risk governance reviews for the largest financial institutions in the US, their attention has turned to the rest of the group. While you may not have developed your own custom scorecard model, you may be using a generic scorecard model to support your credit decisions either for loan origination and/or portfolio management. As a result of the use of even generic scorecards and models, you do have obligations for model risk governance as stated in the guidance. While you may not be basing any decisions strictly on a score alone, the questions you have to asking yourself are: Does my credit policy or underwriting guidelines reference the use of a score in my decision process? While I may not be doing any type of auto-decision, do I restrict any credit authority based upon a score? Do I adjust any thresholds/underwriting guidelines based upon a score that is returned? For example, do I allow a higher debt to income if the score is above a certain level? How long have you been using a score in your decision processes that may have become a significant influence on how you decision credit? As you can see from the questions above, the guidance covers a significant population of the financial institutions in the US. As a result, some of the basic components that your financial institution must demonstrate it has done (or will do) are: Recent validation of the scorecard against your portfolio performance Demonstration of appropriate policy governing the use of credit risk models per the regulation Independence around the authority and review of the model risk governance and validations Proper support and documentation from your generic scorecard provider per the guidance. If you would like to learn more on this topic, please join me at the upcoming RMA Annual Risk Management Conference where I will be speaking on Model Validation for Community Banks on Monday, Oct. 27, 9:30 a.m. – 10:30 a.m. or 11 a.m. – 12 p.m. Also, if you are interested in gaining deeper insight on regulations affecting financial institutions and how to prepare your business, download Experian’s Compliance as a Differentiator perspective paper.

By: Maria Moynihan As consumers, we expect service, don’t we? When service or convenience lessens or is taken away from us altogether, we struggle to comprehend it. As a recent example, I went to the pharmacy the other day and learned that I couldn’t pick up my prescription since the pharmacists were out to lunch. “Who takes lunch anymore?” I thought, but then I realized that too often organizations limit their much needed services as a cost-saving measure. Government is no different. City governments, for instance, may reduce operating hours or slash services to balance budgets better, especially when collectables are maxed out, with little movement. For many agencies, reducing services is the easiest way to offset costs. Often, municipalities offset revenue deficits by optimizing their current collections processes and engaging in new methods of revenue generation. Why then isn’t revenue optimization and modernization being considered more often as a means to offset costs? Some may simply be unsure of how to approach it or unaware of the tools that exist to help. For agencies challenged with collections, there is an option for revenue assurance. With the right data, analytics and technologies, agencies can maximize collection efforts and take advantage of their past-due fines and fees to: Turn stale debt into a new source of revenue by determining the value of their entire debt portfolio and evaluating options for a stale assets sale Reduce delinquencies by better assessing constituents and businesses at the point of transaction and collecting outstanding debt before new services are rendered Minimize current debt by segmenting and prioritizing collection efforts through finding and contacting debtors and gauging their capacity to pay Improve future accounts receivable streams by identifying the best collectable debt for outsourcing What is your agency doing to offset costs and balance budgets better? See what industry experts suggest as best practices for collections, and generate more revenue to keep services fully in place for your constituents.

Collection agencies provide reports with respect to their performance and collection activities. Depending on which system the agencies are using and the extent it has been modified, the reports may look similar, but then again the data and format may be completely different. Finding the common data and comparing the performance of two or more agencies may become a daunting, manual task. Agency management systems have solved that problem by bringing back performance, activity and other data from the agencies back into a common reporting database. This allows for easy comparison through tables and calculations via common data elements. The ability to truly compare data in this way allows for a more analytical “champion/challenger” approach to managing collection agencies. The key to champion/challenger is the ability to easily compare the performance of one or more agencies using like accounts placed at the same time. Tracking allocations of accounts which fall into the same placement strata, split between agencies on the same allocation, makes it easy to compare recoveries of discrete, similar “sample data sets” over time for a more true comparison. These results should lead to the allocation of more accounts of similar types to the champion, less to the challenger. Do you have the systems you need for a champion/challenger approach with respect to your collection agencies? Experian can help with its agency allocation and management solutions through Tallyman Agency Allocation. Learn more about our Tallyman Agency Allocationsoftware.

By: Mike Horrocks A recent industry survey was published that called out the number one reason that lenders were dissatisfied or willing to go to another financial institution (and take their book of business with them) was not compensation. While, compensation is often thought of as the number one driver for this kind of change in your bench of lenders, it had much more to do with being able to serve customers efficiently. One of the key reasons that lenders were unhappy was that they were in a workflow and decisioning process where the lender could not close loans on time, putting stress on the loan officer's relationships and destroying borrower confidence. Thinking of my own experiences as a commercial lender, my interactions with the private bankers, branch managers, and lenders that served every kind of customer, I would absolutely have to agree with this study. Nothing is more disheartening then working on bringing in a client, and then having the process not give me a response in the time that my clients are expecting or that the completion is achieving. Automation in the process is the key. While lenders still will need to be engaged in the process and paying attention to the relationship, it can be significantly refocused to other parts of the business. This leads to benefits such as: Protecting the back office and the consistence of booking and servicing loans. Ensuring that the risk appetite is consistent for the institution for every deal. Growing a portfolio of loans that can and will adhere to sound portfolio management techniques. So how is your process supporting lenders? Are you automating to help in areas that give you a competitive advantage with robust credit scores, decision strategies or risk management solutions that are helping close deals quickly or are you requiring a process that is keeping them from bringing more customers (and profits) in the door? Henry Ford is credited to say, “Coming together is a beginning. Keeping together is progress. Working together is success.” Take a closer look at your lending process. Do you have the tools that help bring your lenders, your customers, and your organization together? If you don’t you may be losing some of your best talent for loan production at a time when you can least afford it.

By: Maria Moynihan At a time when people are accessing information when, where and how they want to, why aren’t voter rolls more up to date? Too often, voter lists aren’t scrubbed for use in mailing, and information included is inaccurate at the time of outreach. Though addresses and other contact information becomes outdated, new address identification and verification has not typically been a resource focus. Costs associated with mandated election-related communications between government and citizens can add up, especially if messages never get to their intended recipients and, in turn, Registrar Offices never get a response. To date, the most common pitfalls with poorly maintained lists have been: Deceased records — where contact information for deceased voters has not been removed or flagged for mailing Email and address errors — where those who have moved or recently changed information failed to update their records, or where errors in the information on file make it unlikely for the United States Postal Service® to reach individuals effectively Duplicate records — where repeat records exist due to update errors or lack of information standardization With resources being tighter than ever, Registrar Offices now are placing emphasis on mailing accuracy and reach. Through third-party-verified data and advanced approaches to managing contact information, Registrar Offices can benefit from truly connecting with their citizens while saving on communication outreach efforts. Experian Public Sector recently helped the Orange County Registrar of Voters increase the quality of its voter registration process. Click here to view the write-up, or stay tuned as I share more on progress being made in this area across states.

One of the challenges that we hear from many of our clients is managing multiple collection agencies in order to recover bad debts. Collection managers who use multiple collection agencies recognize the potential upside to utilizing multiple agencies. Assigning allocate accounts to different agencies based on geography, type of account, status of account (such as a skip), first, second or third placement, and other factors may lead to greater recoveries than just using a single agency. Also, collection managers recognize the advantage of pitting agencies against each other in a positive manner to achieve significantly better results. However this can present a challenge in that the more agencies collection managers use, the greater the risk of losing operational control. Here are some questions to ask before engaging in a multiple collection agency strategy: Do you know which agency has which accounts? Were some accounts accidently assigned to more than one agency? Is it easy to locate an account with an agency if it needs to be withdrawn from it? Is information flowing from one agency to another if agencies are used for second and third placements? Managing multiple agencies can get complex pretty quickly, but rather than just using one agency to avoid these complexities, there is an alternative to consider: Loss of control can be overcome with effective systems that allocate and manage accounts assigned to multiple agencies. These systems allow for the allocation, recall, activity tracking, performance reporting, and commission calculations or vendor audits. No more spreadsheets or other time consuming, error prone manual processes. Experian can help with its agency allocation and management solutions through Tallyman Agency Allocation. Learn more about our Tallyman Agency Allocation software.

by John P. Robertson, Senior Business Process Specialist As a Senior Business Process Specialist for the Experian Decision Analytics, John provides guidance to clients in the areas of profitability strategies for risk based pricing and relationship profitability. He assists banks in developing and implementing successful transitions for commercial lending that improve both the financial efficiency of the lending process and the productivity of the lending officers. John has 26 years of experience in the banking industry, with prior background in cash, treasury, and asset /liability management. For quite some time now, the banking industry has experienced a flat funding curve. Very small spreads have existed between the short and long term rates. Slowly, we have begun to see the onset of a normalized curve. At this writing, the five year FHLB Advance rate is about 2.00%. A simplistic view of loan pricing looks something like this: + Interest Income + Non-Interest Income - Cost of Funds - Non-Interest Expense - Risk Expense = Income before Tax The example is pretty simple and straight forward, “back of the napkin” kind of stuff. We back into a spread needed to reach breakeven on a five year fixed rate loan by using the UBPR (Uniform Bank Performance Report) national peer average for Non-Interest Expense of approximately 3.00%. You would need a pre-tax rate requirement of 5.00% before you consider the risk and before you make any money. If you tack on 1.00% for risk and some kind of return expectation, the rate requirement would put you around a 6.00% offering level. From a lender’s perspective, a 6.00% rate on a minimal risk five year fixed rate loan doesn’t exist. They might as well go home. CFO’s have been asking themselves, “What do we do with this excess cash? We get such a paltry spread. How can we put higher yielding loans on our books at today’s competitive rates? We’ve got plenty of capital even with the new regulation requirements so can we repo the securities and use the net spread for our cost of funds?” Leveraging the excess cash and securities in order to meet the pressing rate demands may be a way banks have been funding selective loans at such low rates on highly competitive, quality loan originations of size. But you have to wonder, what about that old adage, “You don’t short fund long term loans.” Won’t you eventually have to deal with compression and “margin squeeze”? Oh and by the way, aren’t you creating a mismatch in the balance sheet which requires explanation. Are they buying a swap to extend the maturity? If so, are they really making their targeted return? If this is what they are doing, why not just accept a lower return but one that is better than the securities? Share your thoughts with me.