Do consumers pay certain types of credit accounts before others during financial distress? For instance, do they prioritize paying mortgage bills over credit card bills or personal loans? During the Great Recession, the traditional notion of payment priority among multiple credit accounts was upended, throwing strategies employed by financial institutions into disarray. Similarly, current circumstances in the context of COVID-19 might cause sudden shifts in prioritization of payments which might have a dramatic impact on your credit portfolio.
Financial institutions would be better able to forecast and control exposure to credit risk, and to optimize servicing practices such as forbearance and collections treatments if they could understand changing customer payment behaviors and priorities of their existing customers across all open trades. Unfortunately, financial institutions’ data—including their own behavioral data and refreshed credit bureau data–are limited to information about their own portfolio.
Experian data provides insight which complements the financial institutions’ data expanding understanding of consumer payment behavior and priorities spanning all trades. Experian recently completed a study aimed at providing financial institutions valuable insights about their customer portfolios prior to COVID-19 and during the initial months of COVID-19. Using the Experian Ascend Technology Platform™, our data scientists evaluated a random 10% sample of U.S. consumers from its national credit file.
Data from multiple vintages were pulled (June 2006, June 2008 and February 2018) and the payment trends were studied over the subsequent performance period. Experian tabulated the counts of consumers who had various combinations of open and active trade types and selected several trade type combinations with volume to differentiate performance by trade type. The selected combinations collectively span a variety of scenarios involving six trade types (Auto Loans, Bankcard, Student Loan, Unsecured Personal Loans, Retail Cards and First Mortgages). The trade combinations selected accommodate a variety of lenders offering different products.
For each of the consumer groups identified, Experian calculated default rates associated with each trade type across several performance periods. For brevity, this blog will focus on customers identified as of February 2018 and their subsequent performance through February 2020. As the recession evolves and when the economy eventually recovers, we will continue to monitor the impacts of COVID-19 on consumer payment behavior and priorities and share updates to this analysis.
- Consumers with Bankcard, Mortgage, Auto and Retail accounts
Among consumers having open and recently active Bankcard, Mortgage, Auto and Retail accounts, bankcard delinquency was highest throughout the 24-month performance window, followed by Retail. Delinquency rates for Auto and Mortgage were the lowest. During the pre-COVID-19 period, consumers paid their secured loans before their unsecured loans. As demonstrated in the table below, customer payment priority was stable across the entire 24-month period, with no significant shift in payment priorities between trade types.
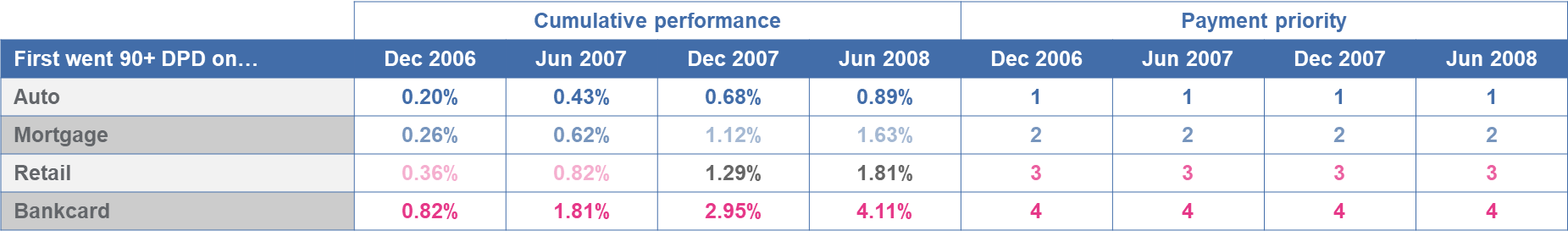
- Consumers with Unsecured Personal Loan, Retail Card and Bankcard accounts.
Among consumers having open and recently active Unsecured Personal Loan, Retail Card and Bankcard accounts, consumers are likely to pay unsecured personal loans first when in financial distress. Retail is the second priority, followed by Bankcard.
KEY FINDINGS
- From February 2018 through April 2020, relative payment priority by trade type has been stable
- Auto and Mortgage trades, when present, show very high payment priority
Download the full Payment Hierarchy Report here.
Download Now
Learn more about how Experian can create a custom payment hierarchy for the customers in your own portfolio, contact your Experian Account Executive, or visit our website.



