
2024 marked a significant year. AI became integral to our workflows, commerce and retail media networks soared, and Google did not deprecate cookies. Amidst these changes, ID bridging emerged as a hot topic, raising questions around identity reliability and transparency, which necessitated industry-wide standards. We believe the latest IAB OpenRTB specifications, produced in conjunction with supply and demand-side partners, set up the advertising industry for more transparent and effective practices.
So, what exactly is ID bridging?
As signals, like third-party cookies, fade, ID bridging emerged as a way for the supply-side to offer addressability to the demand-side. ID bridging is the supply-side practice of connecting the dots between available signals, that were generated in a way that is not the expected default behavior, to understand a user’s identity and communicate it to prospective buyers. It enables the supply-side to extend user identification beyond the scope of one browser or device.
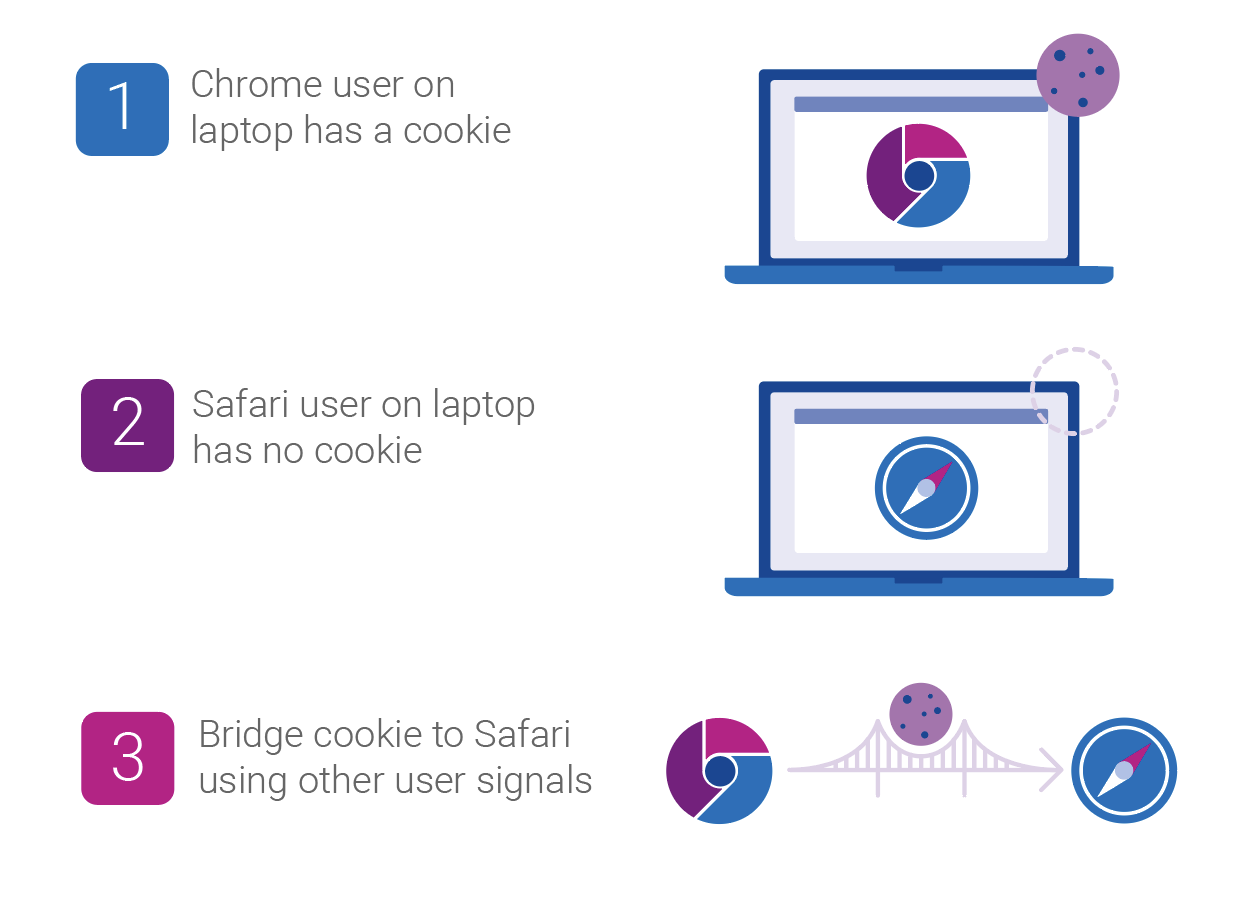
Imagine you visit a popular sports website on your laptop using Chrome. Later, you use the same device to visit the same sports website, but this time, on Safari. By using identity resolution tools, a supply-side partner can infer that both visits are likely from the same user and communicate with them as such.
ID bridging is not inherently a bad thing. However, the practice has sparked debate, as buyers want full transparency into the use of a deterministic identifier versus an inferred one. This complicates measurement and frequency capping for the demand-side. Before OpenRTB 2.6, ID bridging led to misattribution as the demand-side could not attribute ad exposures, which had been served to a bridged ID, to a conversion, which had an ID different from the ad exposure.
OpenRTB 2.6 sets us up for a more transparent future
In 2010, the IAB, along with supply and demand-side partners, formed a consortium known as the Real-Time Bidding Project for companies interested in an open protocol for the automated trading of digital media. The OpenRTB specifications they produced became that protocol, adapting with the evolution of the industry.
The latest evolution, OpenRTB 2.6, sets out standards that strive to ensure transparency in real-time bidding, mandating how the supply-side should use certain fields to more transparently provide data when inferring users’ identities.
What’s new in OpenRTB 2.6?
Here are the technical specifications for the industry to be more transparent when inferring users’ identities:
- Primary ID field: This existing field now can only contain the “buyeruid,” an identifier mutually recognized and agreed upon by both buyer and seller for a given environment. For web environments, the default is a cookie ID, while for app activity, it is a mobile advertising ID (MAID), passed directly from an application downloaded on a device. This approach ensures demand-side partners understand the ID’s source.
- Enhanced identifier (EID) field: The EID field, designated for alternative IDs, now accommodates all other IDs. The EID field now has additional parameters that provide buyers transparency into how the ID was created and sourced, which you can see in the visual below:
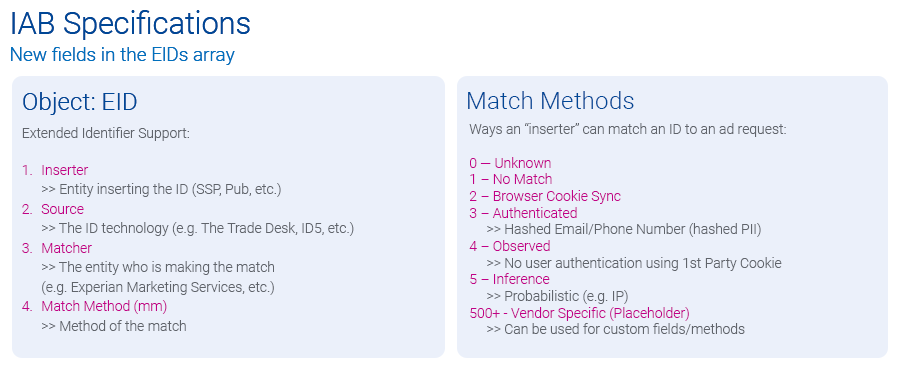
Using the above framework, a publisher who wants to send a cross-environment identifier that likely belongs to the same user would declare the ID as “mm=5,” while listing the potential third-party identity resolution partner under the “matcher” field, which the visual below depicts. This additional metadata gives the demand-side the insights they need to evaluate the reliability of each ID.

“These updates to OpenRTB add essential clarity about where user and device IDs come from, helping buyers see exactly how an ID was created and who put it into the bidstream. It’s a big step toward greater transparency and trust in the ecosystem. We’re excited to see companies already adopting these updates and can’t wait to see the industry fully embrace them by 2025.”
Hillary Slattery, Sr. Director, Programmatic, Product Management, IAB Tech Lab
Experian will continue supporting transparency
As authenticated signals decrease due to cookie deprecation and other consumer privacy measures, we will continue to see a rise in inferred identifiers. Experian’s industry-leading Digital Graph has long supported both authenticated and inferred identifiers, providing the ecosystem with connections that are accurate, scalable, and addressable. Experian will continue to support the industry with its identity resolution products and is supportive of the IAB’s efforts to bring transparency to the industry around the usage of identity signals.
Supply and demand-side benefits of adopting the new parameters in OpenRTB 2.6
- Partner collaboration: Clarity between what can be in the Primary ID field versus the EID field provides clear standards and transparency between buyers and sellers.
- Identity resolution: The supply side has an industry-approved way to bring in inferred IDs while the demand side can evaluate these IDs, expanding addressability.
- Reducing risk: With accurate metadata available in the EID field, demand-side partners can evaluate who is doing the match and make informed decisions on whether they want to act on that ID.
Next steps for the supply and demand-sides to consider
For supply-side and demand-side partners looking to utilize OpenRTB 2.6 to its full potential, here are some recommended steps:
For the supply-side:
- Follow IAB Specs and provide feedback: Ensure you understand and are following transparent practices. Ask questions on how to correctly implement the specifications.
- Vet identity partners: Choose partners who deliver the most trusted and accurate identifiers in the market.
- Be proactive: Have conversations with your partners to discuss how you plan to follow the latest specs, which identity partners you work with, and explain how you plan to provide additional signals to help buyers make better decisions.
We are beginning to see SSPs adopt this new protocol, including Sonobi and Yieldmo.
“The OpenRTB 2.6 specifications are a critical step forward in ensuring transparency and trust in programmatic advertising. By aligning with these standards, we empower our partners with the tools needed to navigate a cookieless future and drive measurable results.”
Michael Connolly, CEO, Sonobi
These additions to the OpenRTB protocol further imbue bidding transactions with transparency which will foster greater trust between partners. Moreover, the data now available is not only actionable, but auditable should a problem arise. Buyers can choose, or not, to trust an identifier based on the inserter, the provider and the method used to derive the ID. While debates within the IAB Tech Lab were spirited at times, they ultimately drove a collaborative process that shaped a solution designed to work effectively across the ecosystem.”
Mark McEachran, SVP of Product Management, Yieldmo
For the demand side:
- Evaluation: Use the EID metadata to assess all the IDs in the EID field, looking closely at the identity vendors’ reliability. Select partners who meet high standards of data clarity and accuracy.
- Collaboration: Establish open communication with supply-side partners and tech partners to ensure they follow the best practices in line with OpenRTB 2.6 guidelines and that there’s a shared understanding of the mutually agreed upon identifiers.
- Provide feedback: As OpenRTB 2.6 adoption grows, consistent feedback from demand-side partners will help the IAB refine these standards.
Moving forward with reliable data and data transparency
As the AdTech industry moves toward a cookieless reality, OpenRTB 2.6 signifies a substantial step toward a sustainable, transparent programmatic ecosystem. With proactive adoption by supply- and demand-side partners, the future of programmatic advertising will be driven by trust and transparency.
Experian, our partners, and our clients know the benefits of our Digital Graph and its support of both authenticated and inferred signals. We believe that if the supply-side abides by the OpenRTB 2.6 specifications and the demand-side uses and analyzes this data, the programmatic exchange will operate more fairly and deliver more reach.
Latest posts

Understand the attitudes, behaviors, motivations and consumer preferences for the five distinct mom segments.

Email marketing is still one of the most effective tools for marketers — especially when paired with mobile. See the stats on why you should make mobile your priority.

Customers willingly give brands their personal information. In exchange, personalization is our duty. Marketers must prove the data is being used to deliver personalized, relevant communication.