Telecommunications, Cable & Utilities
Telecommunications, Cable & Utilities

Understanding the behaviors of best-in-class credit risk managers For financial institutions to achieve superior performance, having the appropriate set of credit risk managers is a prerequisite. The ability to gain insight from data and customer behavior and to use that insight for strategic advantage is a critical ingredient for success. At the same time, the risk-management community is under increasing pressure to understand and explain underlying trends in credit portfolios — and to monitor, interpret and explain these trends with ever-greater accuracy. A common problem financial institutions face when confronting staff resource needs is the difficulty in recruiting and retaining experienced risk-management professionals. The risk-management community is notoriously small, and hiring expertise from within this community is extremely difficult. Skilled risk managers truly are a finite resource, but their skill set is in huge demand. Hiring the right talent is crucial to job satisfaction, leading to higher engagement levels and reduced attrition costs. On top of that, employee engagement is vital to an organization’s success. It drives employee productivity and fosters a culture of innovation, which leads to higher profitability for the entire organization. Building, attracting and retaining risk-management resources requires a commitment to engaging in staff personal development. A great way to support employee engagement is to invest in their personal and professional development, including opportunities for training and team building. If an organization can show that it is committed to developing its people and providing opportunities for career growth, employee engagement levels will rise, with all the benefits this entails. Typically, financial institutions bridge the resource skill gap by either hiring skilled statistical and analytical experts or developing in-house resources. Both of these approaches, however, require significant on-the-job training to teach employees how to link raw statistical techniques and procedures to influencing the profit and loss statement of the business line which they support. The challenge is often broadening the understanding of these skill set “silos” and their contribution to the overall portfolio. By opening that view, the organization generates additional value from these resources as lines of communication are improved and insights and opportunities found within the data are shared more effectively across the organizational team. Experian’s Global Consulting Practice provides a solution to this problem. Our two-day Risk and Portfolio Management Essentials training workshop offers the opportunity to understand the behaviors of best-in-class risk managers. What are the tools and enablers required for the role? How do they prepare for the process of managing credit risk? What areas must risk managers consider managers across the Customer Life Cycle? What differentiates the good from the great? To complement the training modules, Experian® offers an interactive, team-based approach that engages course participants in the build options of a defined portfolio. Participants leverage the best-in-class techniques presented in the sessions in a series of competitive, team-based exercises. This set of cross-organizational exercises drives home the best-in-class techniques and further builds understanding that resonates across the organization long after the course is concluded. For our current offerings, locations and to register click here.

What is blockchain? Blockchain is beginning to get a lot of attention, so I thought it might be time to figure out what it is and what it means. Basically, a blockchain is a permissionless, distributed database that maintains a growing list of records (transactions) in a linear, chronological (and time-stamped) ledger. At a high level, this is how it works. Each computer connected to the network gets a copy of the entire blockchain and performs the task of validating and relaying transactions for the whole chain. The batches of valid transactions added to the record are called “blocks.” A block is the “current” part of a blockchain that records some or all of the recent transactions and once completed goes into the blockchain as a permanent database. Each time a block gets completed, a new block is created, with every block containing a hash of the previous block. There are countless numbers of blocks in the blockchain. To use a conventional banking analogy, the blocks would be a full history of every banking transaction for every person, and the blockchain would be a complete banking history. The entire blockchain is sent to everyone who has access, and every user validates the information in the block. It’s like if Tom, Bob and Harry were standing on the street corner and saw a cyclist hit by a car. Individually, all three men will be asked if the cyclist was struck by the car, and all three will respond “yes.” The cyclist being hit by the car becomes part of the blockchain, and that fact cannot be altered. Blockchain generally is used in the context of bitcoin, where similar uses of the structure are called altchains. Why should I care or, at the very least, pay attention to this movement? Because the idea of it is inching toward the tipping point of mainstream. I recently read an article that identified some blockchain trends that could shape the industry in coming months. The ones I found most interesting were: Blockchain apps will be released Interest in use cases outside payments will pick up Consortia will prove to be important Venture capital money will flow to blockchain start-ups While it’s true that much of the hype around blockchain is coming from people with a vested interest, it is beginning to generate more generalized market buzz as its proponents emphasize how it can reduce risk, improve efficiency and ultimately provide better customer service. Let’s face it, the ability to maintain secure, fast and accurate calculations could revolutionize the banking and investment industries, as well as ecommerce. In fact, 11 major banks recently completed a private blockchain test, exchanging multiple tokens among offices in North America, Europe and Asia over five days. (You can read The Wall Street Journal article here.) As more transactions and data are stored in blockchain or altchain, greater possibilities open up. It’s these possibilities that have several tech companies, like IBM, as well as financial institutions creating what has become known as an open ledger initiative to use the blockchain model in the development of new technologies that will enable a wider array of services. There is no doubt that the concept is intriguing — so much so that even the SEC has approved a plan to issue stock via blockchain. (You can read the Wired article here.) The potential is enough to make many folks giddy. The idea that risk could become a thing of the past because of the blockchain’s immutable historical record — wow. It’s good to be aware and keep an eye on the open ledger initiative, but let’s not forget history, which has taught us that (in the wise words of Craig Newmark), “Crooks are early adopters.” Since blockchain’s original and primary usage has been with bitcoin, I don’t think it is unfair to say that there will be some perceptions to overcome — like the association of bitcoin to activities on the Dark Web such as money laundering, drug-related transactions and funding illegal activities. Until we start to see the application across mainstream use cases, we won’t know how secure blockchain is or how open business and consumers will be to embracing it. In the meantime, remind me again, how long has it taken to get to a point of practical application and more widespread use of biometrics? To learn more, click here to read the original article.

As thought leaders in every industry make predictions for what 2016 will bring, I’m guessing there will be a few constants. New couples will marry. Some couples, sadly, will divorce. Young and old will move – some into first homes – others downsizing or making moves cross-country for work. And waves of individuals will clamor to the latest devices – a new iPhone7, perhaps. The Apple rumors are already flying. Yes, no big surprises, right? But, do you know what all of these very standard life events have in common? These transitions often result in shifts in consumer data, sometimes making people more difficult to track and contact. New last names, new addresses, new phone numbers. Suddenly, the consumer data that companies and lenders have on file are dated, and when it comes time to reach out to these individuals, it’s a challenge to connect. But that is just the beginning. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is increasing its efforts to register consumer complaints and taking aggressive actions to stop companies from making unsolicited phone calls. And the penalties are steep. Fines per individual infraction can be anywhere from $500 to $1,500. Companies have been delivered hefty penalties in the thousands, and in some cases millions, of dollars, over the past few years. All have questions and are seeking to understand how they must adjust their policies and call practices. Now those multiple attempts to call and find a consumer can cost you – big time. No more “shotgun” approaches to identifying and using phones. It’s simply too risky. The Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA), enforced by the FCC, has been around since 1991, but regulations have been closely scrutinized over the past year since the FCC announced a new ruling last summer to clarify hot topics. In their July paper, they aim to communicate the definition of an “auto-dialer,” consent-to-call rules, how to address the reassignment of cell phone numbers, and the new requirement for “one call” without liability. In short, the Declaratory Ruling has opened the door to even greater liability under the TCPA, leaving companies who place outbound customer calls at-risk for compliance violations. Some are projecting the TCPA rules will continue to become even more expansive in 2016, so companies must really assess their call strategies and put best practices in place to increase right-party contact rates. Suggestions include: Identify landline and cell phones for TCPA compliance with dialer campaigns Focus on right- and wrong-party contact to improve customer service Score phones or apply cut-off scores based on the confidence of the number or match Scrub often for updated or verified information Establish a process to identify ported phones Determine when and how often you dial cell phones Provide consumers user-friendly mechanisms– such as texting “STOP” or “UNSUBSCRIBE” – to opt-out of receiving TCPA-covered communications. Review the policies and practices of third-party vendors to ensure they are not sending communications violating the TCPA With the huge advancements in mobile technology and the ever-changing digital landscape, it’s challenging to keep up, but regulators are cracking down on violations, and a slew of lawyers are ready to file on behalf of unhappy consumers dialed one-too-many times. Beyond a best-practice review, tools and systems are available to identify the right number for those moving and changing consumers. And I’m sure we can all agree, those life events will continue to happen in 2016. Marriages, divorces, moves, new devices. They’re coming. As a result, it’s necessary to track the resulting changes to consumer data. Only then will you have a shot at avoiding negative customer experiences and fines.

Leveraging customer intelligence in the age of mass data compromise Hardly a week goes by without the media reporting a large-scale hack of sensitive personal or account information. Increasingly, the public seems resigned to believe that such compromises are the new normal, producing a kind of breach fatigue that may be lowering the expectations consumers have for identity and online security. Still, businesses must be vigilant and continue to apply comprehensive, data-driven intelligence that helps to thwart both breaches and the malicious use of breached information and to protect all parties’ interests. We recently released a new white paper, Data confidence realized: Leveraging customer intelligence in the age of mass data compromise, to help businesses understand how data and technology are needed to strengthen fraud risk strategies through comprehensive customer intelligence. At its core, reliable customer intelligence is based on high-quality contextual identity and device attributes and other authentication performance data. Customer intelligence provides a holistic, bound-together view of devices and identities that equips companies and agencies with the tools to balance cost and risk without increasing transactional friction and affecting the customer experience. In the age of mass data compromise, however, obtaining dependable information continues to challenge many companies, usually because consumer-provided identities aren’t always unique enough to produce fully confident decisioning. For more information, and to get a better sense of what steps you need to take now, download the full white paper.

The financial services industry continues to face mounting pressures to meet the highest standards of data reporting and accuracy. New regulations and mandates are introduced regularly, impacting the way companies do business. And a more credit-educated consumer base is seeking insights into their own credit data, providing a separate second of eyes that demand accuracy. Not only has the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) set requirements on dispute investigation and response, but the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) is also paying close attention. Recent announcements indicate the CFPB wants more information about the credit eco-system to gain more data about consumer disputes. According to the CFPB, it’s a joint problem – “the NCRAA’s, data furnishers, public record providers, and consumers all play roles which affect the accuracy of the information with credit reports.” And it’s not just the big banks that are being targeted with fines. The CFPB has made it clear it will also direct attention to certain nonbanks and financial products. In today’s data-driven environment, there are roughly 12,000-plus data furnishers, resulting in more than one billion pieces of information being updated on a monthly basis. Over 220 million consumers have some form of credit information attached to them, and transactional data is flowing all the time. Fail to update and a furnisher will quickly see flaws in their reporting. In fact, a recent study revealed an estimated 2.1% of contact info goes bad if unattended for more than one month. Clearly, achieving data quality is an ongoing investment for any organization, but companies often lack a clean plan. Some data furnishers fail to report, or elect to report to just one bureau, even though providing better data will result in a more complete and accurate credit profile. So how do you tackle the challenge of data quality? Organizations should consider implementing these six steps: Review data governance. Correct errors in data submissions. Complete an audit of data submissions. Evaluate disputes and resolutions. Compare data to peers and the industry. Review existing policies and processes. Follow these steps and your organization will earn a reputation among both regulators and consumers for clean, credible data. Plus, the investment in better data will reduce the need to resolve future disputes and fines. To learn more about meeting your FCRA responsibilities and best practices around data quality, check out our on-demand webinar or data integrity services site.

It’s official. Millennials have surpassed Baby Boomers in population size, according to the US Census. And while they are quick to adopt the “selfie” and all things social, they have been slow to embrace the world of credit. Sure, there’s been increased regulation over the past decade, and coming into adulthood in the midst of the Great Recession hasn’t helped. But don’t count Millennials out of the credit game just yet. A deeper, more segmented view of this digital-dependent generation shows a very diverse population with plenty of opportunity for lenders. Plus, their sheer size in numbers and $200 billion in annual buying power demand financial institutions evolve to accommodate this massive market. As Gen Y comes of age, there is growing evidence they are open to building and growing their personal credit history. But if financial institutions wish to capture the attention and business of this demographic, they must adapt, leveraging deeper segmentation insights with more effective prospecting strategies to reach them. Experian's data reveals key trends in terms of how this generation is utilizing credit, tips and tools to find the most credit-ready individuals, and strategies to grow the thin-file Millennials as they come of age. “Given the significance millennials play in financial services and the credit marketplace, it is crucial to understand this influential consumer segment and how they use credit as a tool,” said Michele Raneri, vice president of analytics and business development. “While this generation may not look like they are on the right track financially, it’s important to keep in mind that credit scores are built on credit experiences, and while this generation has been slower to use credit, they have plenty of opportunities to build a positive credit history.” To learn more about Millennials and credit, visit Experian.com/millennials.

Electronic signatures and their emerging presence in our Internet-connected world I had the opportunity to represent Experian at the eSignRecords 2015 conference in New York City last week. The concept of electronic signature, while not new, certainly has an emerging presence in the Internet-connected world — as evidenced by the various attendee companies that were represented, everything from home mortgages to automobiles. Much of the discussion focused on the legal aspects of accepting an electronic signature in lieu of an in-person physical signature. The implications of accepting this virtual stamp of approval were discussed, as well as the various cases that already have been tried in court. Of course, the outcome of those cases shapes the future of how to properly integrate this new form of authorization into existing business processes. Attendees discussed the basic concept of simply accepting a signature on an electronic pad as opposed to one written on a piece of paper. That act alone has many legal challenges even though it provides the luxury of in-person authentication through a face-to-face meeting. The complexities and risk increase exponentially when these services are extended over the Internet. The ability to sign documents virtually opens up a whole new world of business opportunities, and the concept certainly caters to the consumer’s need for convenience. However, the anonymity of the Internet presents the everyday challenge of balancing consumer expectations of greater ease of use with necessary fraud prevention measures. Ultimately, it always comes back to understanding who is actually signing that document. All of this highlights the need for robust authentication and security measures. As more and more legal documents and contracts are passed around virtually, the opportunity to properly screen and verify who has access to the documents gets more critical. Many organizations still rely on the tried-and-true method of knowledge-based authentication (KBA), while many others have called for its end. KBA continues to soldier on as an effective way to ensure that people on the other end of the wire are who they say they are by asking questions that — presumably — only they know the answers to. In most cases, KBA is viewed as a “check the box” step in the process to satisfy the lawyers. In certain cases, that’s all you need to do to ensure compliance with legal policy or regulatory requirements. It starts to get tricky is when there’s more on the line than just “check the box” actions. When the liability of first- or third-party fraud, becomes greater than simple compliance, it’s time to implement tighter security, while at the same time limiting the amount of friction caused by the process. Many in attendance discussed the need for layers of authentication based on the type of documents that are being processed and handled. This speaks directly to the point that one size does not fit all. As the industry matures and acceptance of e-signatures increases, so too does the need for more robust, flexible options in authentication. Another topic — that was quite frankly foreign to everyone we talked to — was the need for security around the concept of account takeover. When discussing this type of fraud, most attendees did not even consider this to be a hole in their strategy. Consider this fictional scenario. I’m responsible for mergers and acquisitions for my publicly traded company. I often share confidential information via electronic means, leveraging one of the many electronic signature solutions on the market. I become a victim of a phishing attack and unknowingly provide my login credentials to the fraudster. The fraudster now has access to every electronic document that I have shared with various organizations — most of which have been targets for mergers and acquisitions. Fraudsters are creative. They exploit new technologies — not because they’re trendsetters, but because oftentimes these new technologies fail to consider how fraudsters can benefit from the system. If you are considering adopting e-signature as a formal process, please consider implementing: Flexible levels of authentication based on the risk and liability of the documents that are being presented and what they are protecting FraudNet for Account Takeover, which enhances security around access to these critical documents to protect against data breaches Not only the needs and experiences of your own business, but customer needs as well to enable to the best possible customer interactions If you haven’t considered implementing e-signature technology into your business process, you should — but be sure to have your fraud team present when considering the implementation.

Understanding and managing first party fraud Background/Definitions Wherever merchants, lenders, service providers, government agencies or other organizations offer goods, services or anything of value to the public, they incur risk. These risks include: Credit risk — Loosely defined, credit risk arises when an individual receives goods/services in exchange for a promise of future repayment. If the individual’s circumstances change in a way that prevents him or her from paying as agreed, the provider may not receive full payment and will incur a loss. Fraud risk — Fraud risk arises when the recipient uses deception to obtain goods/services. The type of deception can involve a wide range of tactics. Many involve receiving the goods/services while attributing the responsibility for repayment to someone else. The biggest difference between credit risk and fraud risk is intent. Credit risk usually involves customers who received the goods/services with intent to repay but simply lack the resources to meet their obligation. Fraud risk starts with the intent to receive the goods/services without the intent to repay. Between credit risk and fraud risk lies a hybrid type of risk we refer to as first-party fraud risk. We call this a hybrid form of risk because it includes elements of both credit and fraud risk. Specifically, first party fraud involves an individual who makes a promise of future repayment in exchange for goods/services without the intent to repay. Challenges of first party fraud First party fraud is particularly troublesome for both administrative and operational reasons. It is important for organizations to separate these two sets of challenges and address them independently. The most common administrative challenge is to align first-party fraud within the organization. This can be harder than it sounds. Depending on the type of organization, fraud and credit risk may be subject to different accounting rules, limitations that govern the data used to address risk, different rules for rejecting a customer or a transaction, and a host of other differences. A critical first step for any organization confronting first-party fraud is to understand the options that govern fraud management versus credit risk management within the business. Once the administrative options are understood, an organization can turn its attention to the operational challenges of first-party fraud. There are two common choices for the operational handling of first-party fraud, and both can be problematic. First party fraud is included with credit risk. Credit risk management tends to emphasize a binary decision where a recipient is either qualified or not qualified to receive the goods/services. This type of decision overlooks the recipient’s intent. Some recipients of goods/services will be qualified with the intent to pay. Qualified individuals with bad intentions will be attracted to the offers extended by these providers. Losses will accelerate, and to make matters worse it will be difficult to later isolate, analyze and manage the first party fraud cases if the only decision criteria captured pertained to credit risk decisions. The end result is high credit losses compounded by the additional first party fraud that is indistinguishable from credit risk. First party fraud is included with other fraud types. Just as it’s not advisable to include first party fraud with credit risk, it’s also not a good idea to include it with other types of fraud. Other types of fraud typically are analyzed, detected and investigated based on the identification of a fraud victim. Finding a person whose identity or credentials were misused is central to managing these other types of fraud. The types of investigation used to detect other fraud types simply don’t work for first-party fraud. First party fraudsters always will provide complete and accurate information, and, upon contact, they’ll confirm that the transaction/purchase is legitimate. The result for the organization will be a distorted view of their fraud losses and misconceptions about the effectiveness of their investigative process. Evaluating the operational challenges within the context of the administrative challenges will help organizations better plan to handle first party fraud. Recommendations Best practices for data and analytics suggest that more granular data and details are better. The same holds true with respect to managing first party fraud. First party fraud is best handled (operationally) by a dedicated team that can be laser-focused on this particular issue and the development of best practices to address it. This approach allows organizations to develop their own (administrative) framework with clear rules to govern the management of the risk and its prevention. This approach also brings more transparency to reporting and management functions. Most important, it helps insulate good customers from the impact of the fraud review process. First-party fraudsters are most successful when they are able to blend in with good customers and perpetrate long-running scams undetected. Separating this risk from existing credit risk and fraud processes is critical. Organizations have to understand that even when credit risk is low, there’s an element of intent that can mean the difference between good customers and severe losses. Read here for more around managing first party fraud risk.

Imagine the following scenario: an attacker acquires consumers’ login credentials through a data breach. They use these credentials to test account access and observe account activity to understand the ebbs and flows of normal cash movement – peering into private financial records – verifying the optimal time to strike for the most financial gain. Surveillance and fraud staging are the seemingly benign and often-transparent account activities that fraudsters undertake after an account has been compromised but before that compromise has been detected or money is moved. Activities include viewing balances, changing settings to more effectively cover tracks, and setting up account linkages to stage eventual fraudulent transfers. The unfortunate thing is that the actual theft is often the final event in a series of several fraudulent surveillance and staging activities that were not detected in time. It is the activity that occurs before theft that can severely undermine consumer trust and can devastate a brand’s reputation. Read more about surveillance, staging and the fraud lifecycle in this complimentary whitepaper.

Soaring in the solar energy utility market By: Mike Horrocks and Rod Everson The summer is a great time of the year - it kicks off summer and the time to enjoy the sunshine and explore! It is also for me the recognition that days now are only getting shorter and makes me think about my year goals and am I going to hit them. In this spirit of kicking off summer, I thought I would talk about three opportunities that the utility vertical could and should take advantage of. 1. The future of Solar Photovoltaics (PV) is just getting brighter A recent study called out an expected 25 percent jump in Solar PV installs over the previous year. This is jump is just another in a long line of solar install records. While the overall cost of these installs has dropped, one must ask whether the accessibility is there for everyone. The answer is not yet. A potential opportunity may come in the form of community solar as an advantage over rooftop solar. This scenario involves a utility installing an array of PV cells and then carving out a specific cell for an individual residential customer for lease, crediting his or her bill at a percentage of the cost. 2. Generations are bringing change Just as spring gives way to summer, summer will give way to fall. The same is true in the utility markets on many fronts. At a larger infrastructure scale, utilities have to think about the kind of plants and capital investments they want to make. Another report indicated that 60,000 megawatts of coal energy is going to be retired over the next four years. This obviously will change the capital decision making functions in the industry. At a more personal level, however, there are changes in the consumers and their behaviors as well. Are those changes being accounted for in your organization? Is the next generation of consumers and the products and services it will demand being formulated in your strategy? How will you identify those consumers and secure them as customers? For example, while electrical energy consumption has been decreasing, what would be the impact if there was a revolution in battery technology? What if charging an electric automobile battery became as fast as filling a tank of gas? What if the battery gave you the same mileage range as a tank of gas and did it at a lower cost per mile? Would electric usage spike? 3. Blackouts happen; be prepared The best-laid plans sometimes still cannot account for those acts of God that cause disruptions to the grid. Blackouts happen, and if you don’t have flashlights with new batteries, you will be left in the dark. The same uncertainty is inevitable in the utility vertical. In the 2015 PwC Power and Utility Survey, 3 percent of the respondents said that there would be minor disruptions in business models, with the rest saying the disruptions would range from moderate to very disruptive. In fact, more than 47 percent of respondents said the changes would be very disruptive. What kind of flashlight-and-fresh-batteries strategy will you employ when the lights go out? Are your decision strategies and risk-management practices based on outdated solutions or approaches? Consider whether your business can take advantage of these situations. If you’re not sure, let’s set aside some time to discuss it, and I can share with you how Experian has helped others. There are still many sunny days ahead, but act now before the seasons change and you and your strategies are left out in the cold.

Customer experience strategies for success Sometimes it’s easier to describe something as the opposite of something else. Being “anti-” something can communicate something meaningful. Cultural movements in the past have taken on these monikers: consider the “anti-establishment” or “anti-war” movements. We all need effective anti-virus protection. And there are loads of skin products marketed as “anti-aging”, “anti-wrinkle”, or “anti-blemish.” But when you think about a vision for the customer experience that your company aspires to deliver, this approach of the “anti-X” falls flat. Would you want to aspire to basically “not stink?” Would that inspire you and your team to run through walls to deliver on that grand aspiration? Would it motivate customers to stick with you, buy more of what you sell, and tell others about you? I think not…But it sure seems like many out there indeed do aspire to “not stink.” Sure, there are great companies out there who have a set a high standard for customer experience, placing it at the center of their strategies and their success. Some, like Zappos, started that way from the beginning. Others, like The Ritz-Carlton, realized that they had lost their way and made the commitment to do the hard work of reaching and sustaining excellence. On the other hand, there are hundreds of firms who have a weak commitment to or even understanding of the importance of customer experience to their strategy and performance. Their leaders may give lip service or just pay attention for a few days or hours following the release of reports from leading analysts and firms. They may have posters and slogans that talk about putting the customer first or similar platitudes. These companies probably even have talented and passionate professionals working tirelessly to improve the customer experience in spite of the fact that nobody seems to care much. What these firms lack is a clear customer experience strategy. As nature abhors a vacuum, customers and employees are free to infer or just guess at it. Focusing on customer experience only when a report comes out – and paying special attention only when weak results put the firm near the bottom of the ranking leads people to conclude that all that really matters is to “not stink.” In other words, don’t stand out for being bad…but don’t worry much about being good as it is not important to the company’s strategy or results. I think that this “don’t stink” implicit strategy helps explain a fascinating insight from a Forrester survey in 2013: “80% of executives believe their company is delivering a superior customer experience, yet in 2013 only 8% of companies surveyed received a top grade from their customers.” Many leaders simply have not invested the energy and commitment necessary to define a real customer experience vision that reflects a deep understanding of the role that it plays in the company’s strategy. Beyond setting that vision, there is a big and sustained commitment required to deliver on the vision, measure results, and continuously adjust as customer needs evolve. Like all journeys, a great customer experience starts with one step. Establishing a customer experience strategy is the first one – and “don’t stink” simply stinks as a strategy. Download our recent perspective paper to learn how exceptional customer experience can give companies the competitive edge they need in a market where price, products and services can no longer be a differentiator.
If rumors hold true, Apple Pay will launch in a week. Five of my last six posts had covered Apple’s likely and actual strategy in payments & commerce, and the rich tapestry of control, convenience, user experience, security and applied cryptography that constitutes as the backdrop. What follows is a summation of my views – with a couple of observations from having seen the Apple Pay payment experience up close. About three years ago – I published a similar commentary on Google Wallet that for kicks, you can find here. I hope what follows is a balanced perspective, as I try to cut through some FUD, provide some commentary on the payment experience, and offer up some predictions that are worth the price you pay to read my blog. Source: Bloomua / Shutterstock.com First the criticism. Apple Pay doesn’t go far enough: Fair. But you seem to misunderstand Apple’s intentions here. Apple did not set out to make a mobile wallet. Apple Pay sits within Passbook – which in itself is a wrapper of rewards and loyalty cards issued by third parties. Similarly – Apple Pay is a wrapper of payments cards issued by third parties. Even the branding disappears once you provision your cards – when you are at the point-of-sale and your iPhone6 is in proximity to the reader (or enters the magnetic field created by the reader) – the screen turns on and your default payment card is displayed. One does not need to launch an app or fiddle around with Apple Pay. And for that matter, it’s even more limited than you think. Apple’s choice to leave the Passbook driven Apple Pay experience as threadbare as possible seems an intentional choice to force consumers to interact more with their bank apps vs Passbook for all and any rich interaction. Infact the transaction detail displayed on the back of the payment card you use is limited – but you can launch the bank app to view and do a lot more. Similarly – the bank app can prompt a transaction alert that the consumer can select to view more detail as well. Counter to what has been publicized – Apple can – if they choose to – view transaction detail including consumer info, but only retains anonymized info on their servers. The contrast is apparent with Google – where (during early Google Wallet days) issuers dangled the same anonymized transaction info to appease Google – in return for participation in the wallet. If your tap don’t work – will you blame Apple? Some claim that any transaction failures – such as a non-working reader – will cause consumers to blame Apple. This does not hold water simply because – Apple does not get in between the consumer, his chosen card and the merchant during payment. It provides the framework to trigger and communicate a payment credential – and then quietly gets out of the way. This is where Google stumbled – by wanting to become the perennial fly on the wall. And so if for whatever reason the transaction fails, the consumer sees no Apple branding for them to direct their blame. (I draw a contrast later on below with Samsung and LoopPay) Apple Pay is not secure: Laughable and pure FUD. This article references an UBS note talking how Apple Pay is insecure compared to – a pure cloud based solution such as the yet-to-be-launched MCX. This is due to a total misunderstanding of not just Apple Pay – but the hardware/software platform it sits within (and I am not just talking about the benefits of a TouchID, Network Tokenization, Issuer Cryptogram, Secure Element based approach) including, the full weight of security measures that has been baked in to iOS and the underlying hardware that comes together to offer the best container for payments. And against all that backdrop of applied cryptography, Apple still sought to overlay its payments approach over an existing framework. So that, when it comes to risk – it leans away from the consumer and towards a bank that understands how to manage risk. That’s the biggest disparity between these two approaches – Apple Pay and MCX – that, Apple built a secure wrapper around an existing payments hierarchy and the latter seeks to disrupt that status quo. Let the games begin: Consumers should get ready for an ad blitz from each of the launch partners of Apple Pay over the next few weeks. I expect we will also see these efforts concentrated around pockets of activation – because setting up Apple Pay is the next step to entering your Apple ID during activation. And for that reason – each of those launch partners understand the importance of reminding consumers why their card should be top of mind. There is also a subtle but important difference between top of wallet card (or default card) for payment in Apple Pay and it’s predecessors (Google Wallet for example). Changing your default card was an easy task – and wholly encapsulated – within the Google Wallet app. Where as in Apple Pay – changing your default card – is buried under Settings, and I doubt once you choose your default card – you are more likely to not bother with it. And here’s how quick the payment interaction is within Apple Pay (takes under 3 seconds) :- Bring your phone in to proximity of the reader. Screen turns on. Passbook is triggered and your default card is displayed. You place your finger and authenticate using TouchID. A beep notes the transaction is completed. You can flip the card to view a limited transaction detail. Yes – you could swipe down and choose another card to pay. But unlikely. I remember how LevelUp used very much the same strategy to signup banks – stating that over 90% of it’s customers never change their default card inside LevelUp. This will be a blatant land grab over the next few months – as tens of millions of new iPhones are activated. According to what Apple has told it’s launch partners – they do expect over 95% of activations to add at least one card. What does this mean to banks who won’t be ready in 2014 or haven’t yet signed up? As I said before – there will be a long tail of reduced utility – as we get in to community banks and credit unions. The risk is amplified because Apple Pay is the only way to enable payments in iOS that uses Apple’s secure infrastructure – and using NFC. For those still debating whether it was a shotgun wedding, Apple’s approach had five main highlights that appealed to a Bank – Utilizing an approach that was bank friendly (and to status quo) : NFC Securing the transaction beyond the prerequisites of EMV contactless – via network tokenization & TouchID Apple’s preference to stay entirely as an enabler – facilitating a secure container infrastructure to host bank issued credentials. Compressing the stack: further shortening the payment authorization required of the consumer by removing the need for PIN entry, and not introducing any new parties in to the transaction flow that could have introduced delays, costs or complexity in the roundtrip. Clear description of costs to participate – Free is ambiguous. Free leads to much angst as to what the true cost of participation really is(Remember Google Wallet?). Banks prefer clarity here – even if it means 15bps in credit. As I wrote above, Apple opting to strictly coloring inside the lines – forces the banks to shoulder much of the responsibility in dealing with the ‘before’ and ‘after’ of payment. Most of the bank partners will be updating or activating parts of their mobile app to start interacting with Passbook/Apple Pay. Much of that interaction will use existing hooks in to Passbook – and provide richer transaction detail and context within the app. This is an area of differentiation for the future – because those banks who lack the investment, talent and commitment to build a redeeming mobile services approach will struggle to differentiate on retail footprint alone. And as smarter banks build entirely digital products for an entirely digital audience – the generic approaches will struggle and I expect at some point – that this will drive bank consolidation at the low end. On the other hand – if you are an issuer, the ‘before’ and ‘after’ of payments that you are able to control and the richer story you are able to weave, along with offline incentives – can aid in recapture. The conspicuous and continued absence of Google: So whither Android? Uniformity in payments for Android is as fragmented as the ecosystem itself. Android must now look at Apple for lessons in consistency. For example, how Apple uses the same payment credential that is stored in the Secure Element for both in-person retail transactions as well as in-app payments. It may look trivial – but when you consider that Apple came dangerously close (and justified as well) in its attempt to obtain parity between those two payment scenarios from a rate economics point of view from issuers – Android flailing around without a coherent strategy is inexcusable. I will say this again: Google Wallet requires a reboot. And word from within Google is that a reboot may not imply a singular or even a cohesive approach. Google needs to swallow its pride and look to converge the Android payments and commerce experience across channels similar to iOS. Any delay or inaction risks a growing apathy from merchants who must decide what platform is worth building or focusing for. Risk vs Reward is already skewed in favor of iOS: Even if Apple was not convincing enough in its attempt to ask for Card Present rates for its in-app transactions – it may have managed to shift liability to the issuer similar to 3DS and VBV – that in itself poses an imbalance in favor of iOS. For a retail app in iOS – there is now an incentive to utilize Apple Pay and iOS instead of all the other competing payment providers (Paypal for example, or Google Wallet) because transactional risk shifts to the issuer if my consumer authenticates via TouchID and uses a card stored in Apple Pay. I have now both an incentive to prefer iOS over Android as well as an opportunity to compress my funnel – much of my imperative to collect data during the purchase was an attempt to quantify for fraud risk – and the need for that goes out of the window if the customer chooses Apple Pay. This is huge and the repercussions go beyond Android – in to CNP fraud, CRM and loyalty. Networks, Tokens and new end-points (e.g. LoopPay): The absence of uniformity in Android has provided a window of opportunity for others – regardless of how fragmented these approaches be. Networks shall parlay the success with tokenization in Apple Pay in to Android as well, soon. Prime example being: Loop Pay. If as rumors go – Samsung goes through with baking in Loop Pay in to its flagship S6, and Visa’s investment translates in to Loop using Visa tokenization – Loop may find the ubiquity it is looking for – on both ends. I don’t necessarily see the value accrued to Samsung for launching a risky play here: specifically because of the impact of putting Loop’s circuitry within S6. Any transaction failure in this case – will be attributed to Samsung, not to Loop, or the merchant, or the bank. That’s a risky move – and I hope – a well thought out one. I have some thoughts on how the Visa tokenization approach may solve for some of the challenges that Loop Pay face on merchant EMV terminals – and I will share those later. The return of the comeback: Reliance on networks for tokenization does allay some of the challenges faced by payment wrappers like Loop, Coin etc – but they all focus on the last mile and tokenization does little more for them than kicking the can down the road and delaying the inevitable a little while more. The ones that benefit most are the networks themselves – who now has wide acceptance of their tokenization service – with themselves firmly entrenched in the middle. Even though the EMVCo tokenization standard made no assumptions regarding the role of a Token Service Provider – and in fact Issuers or 3rd parties could each pay the role sufficiently well – networks have left no room for ambiguity here. With their role as a TSP – networks have more to gain from legitimizing more end points than ever before – because these translate to more token traffic and subsequently incremental revenue – transactional and additional managed services costs (OBO – On behalf of service costs incurred by a card issuer or wallet provider). It has never been a better time to be a network. I must say – a whiplash effect for all of us – who called for their demise with the Chase-VisaNet deal. So my predictions for Apple Pay a week before its launch: We will see a substantial take-up and provisioning of cards in to Passbook over the next year. Easy in-app purchases will act as the carrot for consumers. Apple Pay will be a quick affair at the point-of-sale: When I tried it few weeks ago – it took all of 3 seconds. A comparable swipe with a PIN (which is what Apple Pay equates to) took up to 10. A dip with an EMV card took 23 seconds on a good day. I am sure this is not the last time we will be measuring things. The substantial take-up on in-app transactions will drive signups: Consumers will signup because Apple’s array of in-app partners will include the likes of Delta – and any airline that shortens the whole ticket buying experience to a simple TouchID authentication has my money. Apple Pay will cause MCX to fragment: Even though I expect the initial take up to be driven more on the in-app side vs in-store, as more merchants switch to Apple Pay for in-app, consumers will expect a consistency in that approach across those merchants. We will see some high profile desertions – driven partly due to the fact that MCX asks for absolute fealty from its constituents, and in a rapidly changing and converging commerce landscape – that’s just a tall ask. In the near-term, Android will stumble: Question is if Google can reclaim and steady its own strategy. Or will it spin off another costly experiment in chasing commerce and payments. The former will require it to be pragmatic and bring ecosystem capabilities up to par – and that’s a tall ask when you lack the capacity for vertical integration that Apple has. And from the looks of it – Samsung is all over the place at the moment. Again – not confidence inducing. ISIS/SoftCard will get squeezed out of breath: SoftCard and GSMA can’t help but insert themselves in to the Apple Pay narrative by hoping that the existence of a second NFC controller on the iPhone6 validates/favors their SIM based Secure Element approach and indirectly offers Softcard/GSMA constituents a pathway to Apple Pay. If that didn’t make a lick of sense – It’s like saying ‘I’m happy about my neighbor’s Tesla because he plugs it in to my electric socket’. Discover how an Experian business consultant can help you strengthen your credit and risk management strategies and processes: http://ex.pn/DA_GCP This post originally appeared here.
Both Visa and MasterCard announced their support for Host Card Emulation (HCE) and their intent to release HCE specifications soon. I have been talking about HCE from late 2012 (partly due to my involvement with SimplyTapp) and you could read as to why HCE matter and what Android KitKat-HCE announcement meant for payments. But in light of the network certification announcements yesterday, this post is an attempt to provide some perspective on what the Visa/MasterCard moves mean, how do their approaches differ in certifying payments using cloud hosted credentials, what should issuers expect from a device and terminal support perspective, why retailers should take note of the debate around HCE and ultimately – the role I expect Google to continue to play around HCE. All good stuff. First, what do the Visa/MasterCard announcements mean? It means that it’s time for banks and other issuers to stop looking for directions. The network announcements around HCE specifications provide the clarity required by issuers to meaningfully invest in mobile contactless provisioning and payment. Further, it removes some of the unfavorable economics inherited from a secure element-centric model, who were forced to default to credit cards with higher interchange in the wallet. Renting space on the secure element cost a pretty penny and that is without taking operational costs in to consideration, and as an issuer if you are starting in the red out of the gate, you were not about to put a Durbin controlled debit card in the wallet. But those compulsions go with the wind now, as you are no longer weighed down by these costs and complexities on day one. And further, the door is open for retailers with private label programs or gift cards to also look at this route with a lot more interest. And they are. MasterCard mentioned bank pilots around HCE in its press release, but MCX is hardly the only retailer payment initiative in town. Let me leave it at that. How do the Visa/MasterCard specs differ? From the press releases, some of those differences are evident – but I believe they will coalesce at some point in the future. MasterCard’s approach speaks to mobile contact-less as the only payment modality, whereas Visa refers to augmenting the PayWave standard with QR and in-app payments in the future. Both approaches refer to payment tokens (single or multi-use) and one can expect them to work together with cloud provisioned card profiles, to secure the payment transaction and verify transactional integrity. To MasterCard’s benefit – it has given much thought to ensuring that these steps – provisioning the card profile, issuing payment tokens et al – are invisible to the consumer and therefore refrains from adding undue friction. I am a purist at heart – and I go back to the first iteration of Google Wallet – where all I had to do to pay was turn on the screen and place the device on the till. That is the simplicity to beat for any issuer or retailer payment experiences when using contactless. Otherwise, they are better off ripping out the point-of-sale altogether. MasterCard’s details also makes a reference to a PIN. The PIN will not be verified offline as it would have been if a Secure Element would have been present in the device, rather – it would be verified online which tells me that an incorrect PIN if input would be used to create an “incorrect cryptogram” which would be rejected upstream. Now I am conflicted using a PIN at the point of sale for anything – to me it is but a Band-Aid, it reflects the inability to reduce fraud without introducing friction. Visa so far seems to be intentionally light on details around mandating a PIN, and I believe not forcing one would be the correct approach – as you wouldn’t want to constrain issuers to entering a PIN as means to do authentication, and instead should have laid down the requirements but left it to the market to decide what would suffice – PIN, biometrics et al. Again – I hope these specs will continue to evolve and move towards a more amenable view towards customer authentication. Where do we stand with device and terminal support? All of this is mute if there are not enough devices that support NFC and specifically – Android KitKat. But if you consider Samsung devices by themselves (which is all one should consider for Android) they control over 30% of the NA market – 44.1 million devices sold in 2013 alone. Lion share of those devices support NFC out of the box – including Galaxy Note II and 3, Galaxy S3 and S4 – and their variants mini, Active, Xoom et al. And still, the disparity in their approach to secure elements, continuing lack of availability in standards and Android support – Tap and Pay was largely a dream. What was also worrisome is that 3 months after the launch of Android KitKat – it still struggles under 2% in device distribution. That being said, things are expected to get markedly better for Samsung devices at least. Samsung has noted that 14 of its newer devices will receive KitKat. These devices include all the NFC phones I have listed above. Carriers must follow through quickly (tongue firmly in cheek) to deliver on this promise before customers with old S3 devices see their contracts expire and move to a competitor (iPhone 6?). Though there was always speculation as to whether an MNO will reject HCE as part of the Android distribution, I see that as highly unlikely. Even carriers know a dead horse when they see one, and Isis’s current model is anything but one. Maybe Isis will move to embrace HCE. And then there is the issue of merchant terminals. When a large block of merchants are invested in upending the role of networks in the payment value chain – that intent ripples far and wide in the payments ecosystem. Though it’s a given that merchants of all sizes can expect to re-terminalize in the next couple of years to chip & pin (with contactless under the hood) – it is still the prerogative of the merchant as to whether the contactless capability is left turned on or off. And if merchants toe Best Buy’s strategy in how it opted to turn it off store-wide, then that limits the utility of an NFC wallet. And why wouldn’t they? Merchants have always viewed “Accept all cards” to also mean “Accept all cards despite the form factor” and believes that contactless could come to occupy a higher interchange tier in the future – as questions around fraud risk are sufficiently answered by the device in real-time. This fear is though largely unsubstantiated, as networks have not indicated that they could come to view mobile contact-less as being a “Card Present Plus” category that charges more. But in the absence of any real assurances, fear, uncertainty and doubt runs rampant. But what could a retailer do with HCE? If re-terminalization is certain, then retailers could do much to explore how to leverage it to close the gap with their customer. Private label credit, closed loop are viable alternatives that can be now carried over contactless – and if previously retailers were cut out of the equation due to heavy costs and complexity for provisioning cards to phones, they have none of those limitations now. A merchant could now fold in a closed loop product (like a gift card) in to their mobile app – and accept those payments over contact-less without resorting to clunky QR or barcode schemes. There is a lot of potential in the closed loop space with HCE, that Retailers are ignoring due to a “scorched earth” approach towards contactless. But smarter merchants are asking ‘how’. Finally, what about Google? Google deserves much praise for finally including HCE in Android and paving the way for brands to recognize the opportunity and certify the approach. That being said, Google has no unequal advantage with HCE. In fact, Google has little to do with HCE going forward, despite GoogleWallet utilization of HCE in the future. I would say – HCE has as much to do with Google going forward, as Amazon’s Kindle Fire has to do with Android. Banks and Retailers have to now decide what this means for them – and view HCE as separate to Google – and embrace it if they believe it has potential to incent their brands to remain top of wallet, and top of mind for the consumer. It is a level playing field, finally. Where do you go next? Indeed – there is a lot to take in – starting with HCE’s role, where it fit in to your payment strategy, impact and differences in Visa/MasterCard approaches, weaving all of these in to your mobile assets while not compromising on customer experience. Clarity and context is key and we can help with both. Reach out to us for a conversation. HCE is a means to an end – freeing you from the costs and complexities of leveraging contactless infrastructure to deliver an end-to-end mobile experience, but there is still the question of how your business should evolve to cater to the needs of your customers in the mobile channel. Payment is after all, just one piece of the puzzle.

By: Teri Tassara In my blog last month, I covered the importance of using quality credit attributes to gain greater accuracy in risk models. Credit attributes are also powerful in strengthening the decision process by providing granular views on consumers based on unique behavior characteristics. Effective uses include segmentation, overlay to scores and policy definition – across the entire customer lifecycle, from prospecting to collections and recovery. Overlay to scores – Credit attributes can be used to effectively segment generic scores to arrive at refined “Yes” or “No” decisions. In essence, this is customization without the added time and expense of custom model development. By overlaying attributes to scores, you can further segment the scored population to achieve appreciable lift over and above the use of a score alone. Segmentation – Once you made your “Yes” or “No” decision based on a specific score or within a score range, credit attributes can be used to tailor your final decision based on the “who”, “what” and “why”. For instance, you have two consumers with the same score. Credit attributes will tell you that Consumer A has a total credit limit of $25K and a BTL of 8%; Consumer B has a total credit limit of $15K, but a BTL of 25%. This insight will allow you to determine the best offer for each consumer. Policy definition - Policy rules can be applied first to get the desirable universe. For example, an auto lender may have a strict policy against giving credit to anyone with a repossession in the past, regardless of the consumer’s current risk score. High quality attributes can play a significant role in the overall decision making process, and its expansive usage across the customer lifecycle adds greater flexibility which translates to faster speed to market. In today’s dynamic market, credit attributes that are continuously aligned with market trends and purposed across various analytical are essential to delivering better decisions.
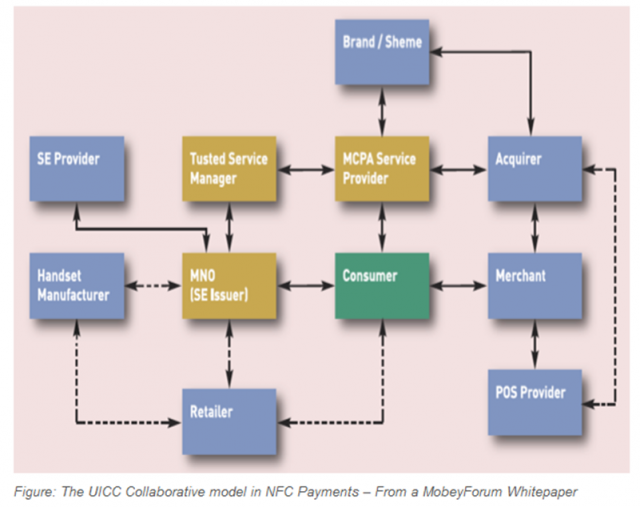
When I wrote about Host Card Emulation back in March, it provoked much debate around whether this capability will die on the cutting floor or be meaningfully integrated in to a future Android iteration. And now that it has, this post is an attempt to look forward, even though much of it is speculative. But I will provide some perspective from a number of conversations I had in the last week with Networks, Issuers, TSMs, Merchants, Platform Owners and EMV practitioners and provide some insight in to perceptions, impacts and the road ahead for NFC. And I will provide some context to why HCE matters to each of these players. First – if you haven’t read my previous post on HCE – this would be a good time to do so. Media has unfortunately focused yet again on the controversy in light of the KitKat HCE announcement – focusing on the end-run around Carriers rather than the upside this brings to those who have been disincentivized previously to consider NFC. What they all seem to have missed is that HCE allows for the following: it reduces the gap between merchants and card issuance, brings the topic of closed-loop and contactless in focus, and more tactically – allows for an easy deployment scenario that does not require them to change the software inside the terminal. I hope those three things do not get lost in translation. Google: Being a Platform Owner for once The Android team deserves much credit for enabling support for Host Card Emulation in KitKat. Beyond the case for platform support – something Blackberry already had – there were both altruistic and selfish reasons for going this route. The former – altruistic – had to do with throwing open another door that would invite third party developers to build on an open NFC stack – while firmly shutting other ones (read criticism from Ars that Android is quickly becoming a closed source – partly through its Play services approach). It was time it acted like a platform owner. And being one entailed democratizing access to tap-and-pay. Selfish – because for the more than 200M Android devices that shipped with NFC support – a fraction of these are tap-and-pay worthy. It had become absurd that one must enquire upon Carrier, Platform, Issuer and Device support before installing an NFC payment app, much less use it. Talk about fragmentation. This was a problem only Google could begin to fix – by removing the absurd limitations put in place in the name of security – but in truth existed because of profit, control and convenience. Google’s role hardly ends here. Today – Host Card Emulation – by definition alone, is reserved as a technical topic. Out of the gate, much needs to be done to educate Issuers and Merchants as to why this matters. For retailers – used to much cynicism in matters relating to NFC – Host Card Emulation offers an opportunity to develop and deploy a closed-loop contactless scheme using retailer’s preferred payment sources – private label, debit, credit and in that order. HCE to Merchants: Friend or Foe? In my opinion – merchants stand to benefit most from HCE. Which is another reason why Google really embraced this concept. Despite having certain benefits for Issuers to provision cards without having to pay the piper, Google had its eyes set on expanding the offline footprint for GoogleWallet and to successfully do so – needed to focus on the merchant value prop while dialing back on what retailers once called the “data donation agreement”. Where merchants primarily struggle today in mobile – is not in replicating the plastic model – it is to create a brand new loyalty platform where the customer sets a payment source and forgets it – preferably one that’s preferred by the merchant – for example a private label card or debit. Except, no open loop wallets had actually centered itself around this premise so far. Google Wallet launched with Citi, then reverted to a negative margin strategy – by charging the merchant CP rates while paying the Issuers CNP rates. It wasn’t ideal – as merchants did not want Google anywhere near the transaction value chain. Meanwhile – it gave Google quite the heartburn to see Apple being successful with Passbook – requiring merchants give nothing back in return for leveraging it to deliver geo-targeted offers and loyalty. This silent takedown must have forced Google’s hands in getting serious about building a complete offer, loyalty, payment scheme that is collaborative (HCE support was a collaborative effort introduced by SimplyTapp) and merchant friendly. I believe HCE support now represents a serious effort to help merchants commercialize a closed-loop advantage in contactless without requiring software changes inside the terminal. Contactless was out of bounds for merchants till now. Not anymore. Having fielded a number of calls from retailers as to what this means, I will distill retailer reactions down to this: measured optimism, casual pessimism and “network” cynicism. Retailers have always looked at EMV and terminalization as a head-fake for NFC – to further lay down the tracks for another three decades of control around pricing and what they see as anti-competitive behavior. Though HCE is in no way tethered to NFC (it’s agnostic of a communication method) – due to its current close association with NFC, merchants see the conversation as a non-starter – until there is a constructive dialogue with networks. At the same time, merchants are cautiously optimistic about the future of HCE – provided that there is a standards body that provides them equal footing with Platform owners, Issuers and networks – to dictate its scope and future. As the platform owner – Google should work with the merchant body, networks, issuers and other stakeholders to see this through. It was not a surprise that those who I talked to all agreed about one thing: that Carriers really should have no role to play in this framework. TSM’s/SE Providers: Where to from here? The nine party model is dead, or will be very soon – as the SE rental model has been shown as previously not being sustainable – and now with HCE – simply wasteful. TSM’s had been focused outside of US for the last several years – as the lack of meaningful commercial launches meant that the US market will simply not bring scale for many years. And with Google shifting away from using a Secure Element in its flagship Nexus models – the writing was already on the wall. TSM’s will look to extend their capabilities in to non-traditional partnerships (Gemalto/MCX) and in to non-hardware scenarios (competing with Cloud SE providers like SimplyTapp in the HCE model). Bell-ID is such an example – and quite likely the only example right now. Networks: Certify or Not? What does Host Card Emulation mean to V/MA? It is no secret that the networks had more than toyed with the idea of software card emulation these last couple of years – realizing the rapidly shrinking runway for NFC. Focus for networks should be now to certify the new approach, as a legitimate way to store and transfer credentials. It’s interesting to hear how our neighbors in the north have reacted to this news. There is still ambiguity among Canadian issuers and networks as to what this means – including debates as to whether an onboard SE is still required for secure storage. That ambiguity will not dissipate till V/MA step in and do their part. I must quote an EMV payments consultant from the north who wrote to me this week: “My boss calls the TSM model “traditional” and I remind him in NFC payments there is no tradition… I think for some people the Global Platform standards with the TSM smack in the middle are like a comfort food – you know what you are getting and it feels secure (with 1000′s of pages of documentation how could they not be!)” That should give GP and TSMs some comfort. Device Support for HCE: What does that look like? Google does not report sales figures on Nexus 4, Nexus 5, Google Play editions of Samsung Galaxy S4 and HTC One – the four devices that are slated to receive KitKat over the next few weeks (apart from the Nexus tablets). So if I would venture a guess – I would say approx 20M devices in total that has NFC capability that will support Host Card Emulation soon. That may not seem much – but it’s a strong base . There is also a possibility that post-Galaxy Nexus devices from Samsung may leapfrog 4.3 to go directly to KitKat. If that happens – just based on reported sales volumes for Galaxy S3 and S4 – that would be a total of 100M devices with NFC support. What does that mean for Samsung’s revenue model around SE – who has an embedded SE from Oberthur in the S3 & S4 devices, which it hopes to charge rent to Visa and others – that’s unclear at this point. Issuers: ISIS alternative or more? For those issuers who passed on Isis, or those who were scorned by Isis – this enables them to outfit their current mobile assets with a payment feature. I wrote about the absurdity in a contactless transaction where the consumer has to close his merchant or banking app and switch to Isis to tap-and-pay – instead of equipping merchant/bank apps with a tap-and-pay feature. HCE means a lot more for Private label Issuers – who have a very inspired base of merchants looking to bridge the gap between private label cards and mobile – and now have an alternative to clumsy, costly and complex orchestrations for provisioning cards – replaced with an easy integration and cheaper deployment. More about that later. Finally, Carriers & Isis: Fight or Flight? God Speed.