Uncategorized

Prescriptive solutions: Get the Rx for your right course of action By now, everyone is familiar with the phrase “big data” and what it means. As more and more data is generated, businesses need solutions to help analyze data, determine what it means and then assist in decisioning. In the past, solutions were limited to simply describing data by creating attributes for use in decisioning. Building on that, predictive analytics experts developed models to predict behavior, whether that was a risk model for repayment, a propensity model for opening a new account or a model for other purposes. The next evolution is prescriptive solutions, which go beyond describing or predicting behaviors. Prescriptive solutions can synthesize big data, analytics, business rules and strategies into an environment that provides businesses with an optimized workflow of suggested options to reach a final decision. Be prepared — developing prescriptive solutions is not simple. In order to fully harness the value of a prescriptive solution, you must include a series of minimum capabilities: Flexibility — The solution must provide users the ability to make quick changes to strategies to adjust to market forces, allowing an organization to pivot at will to grow the business. A system that lacks agility (for instance, one that relies heavily on IT resources) will not be able to realize the full value, as its recommendations will fall behind current market needs. Expertise — Deep knowledge and a detailed understanding of complex business objectives are necessary to link overall business goals to tactical strategies and decisions made about customers. Analytics — Both descriptive and predictive analytics will play a role here. For instance, the use of a layered score approach in decisioning — what we call dimensional decisioning — can provide significant insight into a target market or customer segment. Data — It is assumed that most businesses have more data than they know what to do with. While largely true, many organizations do not have the ability to access and manage that data for use in decision-making. Data quality is only important if you can actually make full use of it. Let’s elaborate on this last point. Although not intuitive, the data you use in the decision-making process should be the limiting factor for your decisions. By that, I mean that if you get the systems, analytics and strategy components of the equation right, your limitation in making decisions should be data-driven, and not a result of another part of the decision process. If your prescriptive environment is limited by gaps in flexibility, expertise or analytic capabilities, you are not going to be able to extract maximum value from your data. With greater ability to leverage your data — what I call “prescriptive capacity” — you will have the ability to take full advantage of the data you do have. Taking big data from its source through to the execution of a decision is where prescriptive solutions are most valuable. Ultimately, for a business to lead the market and gain a competitive advantage over its competitors — those that have not been able to translate data into meaningful decisions for their business — it takes a combination of the right capabilities and a deep understanding of how to optimize the ecosystem of big data, analytics, business rules and strategies to achieve success.

We are excited to announce that Experian Fraud and Identity Solutions is presenting at FinovateFall 2016! Finovate conferences showcase cutting-edge banking and financial technology in a unique demo-only format. Held twice a year, the conferences bring together the leaders from top financial institutions, fintech companies, investors from around the globe, and fintech media to share and promote the most innovative financial technology solutions. "Experian’s Fraud and Identity Solutions is a leader in customer-centric identity and fraud solutions, providing fraud management solutions to some of the world’s largest brands in financial services, insurance, and retail," said Adam Fingersh, general manager and senior vice president of Fraud and Identity Solutions in North America. "We will introduce our Fraud and Identity Solutions and promote our newly released CrossCore platform. CrossCore puts more control in the hands of fraud teams to adapt and deploy strategies that keep up with the pace of fraud while reducing burdens on IT and data science teams." Fingersh and John Sarreal, senior director of Fraud and Identity product management at Experian, are presenting the 7-minute demo focusing on the key CrossCore capabilities, and how CrossCore manages fraud and identity services through its flexible API; open, plug-and-play platform; and powerful workflow and strategy design capabilities. In Forrester’s 2016 “Vendor Landscape: Mobile Fraud Management”, Experian Fraud and Identity Solutions was cited as having the most capabilities and one of the highest estimated revenues in total fraud management in the market, between $200 million and $250 million. Join us for the event on September 8-9 in New York. Experian also has an exclusive 20% off discount code (Experian20FF16) to get even more savings! For more information on the event or to view videos of previous demos, please visit finovate.com.

Is the speed of fraud threatening your business? Like many other fraud and compliance teams, your teams may be struggling to keep up with new business dynamics. The following trends are changing the way consumers do business with you: 35 percent year-over-year growth in mobile commerce More than $27 billion forecasted value of mobile payment transactions in 2016 45 percent of smartphone owners using a mobile device to make a purchase every month More than 1 billion mobile phone owners will use their devices for banking purposes by the end of 2015 In an attempt to stay ahead of fraud, systems have become more complex, more expensive and even more difficult to manage, leading to more friction for your customers. How extensive is this impact? 30 percent of online customers are interrupted to catch one fraudulent attempt One in 10 new applicants may be an imposter using breached data $40 billion of legitimate customer sales are declined annually because of tight rules, processes, etc. This rapid growth only reinforces the need for aggressive fraud prevention strategies and adoption of new technologies to prepare for the latest emerging cybersecurity threats. Businesses must continue their efforts to protect all parties’ interests. Fraudsters have what they need to be flexible and quick. So why shouldn’t businesses? Introducing CrossCore™, the first smart plug-and-play platform for fraud and identity services. CrossCore uses a single access point to integrate technology from different providers to address different dangers. When all your fraud and identity solutions work together through a single application program interface, you reduce friction and false positives — meaning more growth for your business. View our recent infographic on global fraud trends

Part four in our series on Insights from Vision 2016 fraud and identity track It was a true honor to present alongside Experian fraud consultant Chris Danese and Barbara Simcox of Turnkey Risk Solutions in the synthetic and first-party fraud session at Vision 2016. Chris and Barbara, two individuals who have been fighting fraud for more than 25 years, kicked off the session with their definition of first-party versus third-party fraud trends and shared an actual case study of a first-party fraud scheme. The combination of the qualitative case study overlaid with quantitative data mining and link analysis debunked many myths surrounding the identification of first-party fraud and emphasized best practices for confidently differentiating first-party, first-pay-default and synthetic fraud schemes. Following these two passionate fraud fighters was a bit intimidating, but I was excited to discuss the different attributes included in first-party fraud models and how they can be impacted by the types of data going into the specific model. There were two big “takeaways” from this session for me and many others in the room. First, it is essential to use the correct analytical tools to find and manage true first-party fraud risk successfully. Using a credit score to identify true fraud risk categorically underperforms. BustOut ScoreSM or other fraud risk scores have a much higher ability to assess true fraud risk. Second is the need to for a uniform first-party fraud bust-out definition so information can be better shared. By the end of the session, I was struck by how much diversity there is among institutions and their approach to combating fraud. From capturing losses to working cases, the approaches were as unique as the individuals in attendance This session was both educational and inspirational. I am optimistic about the future and look forward to seeing how our clients continue to fight first-party fraud.

On June 2, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) proposed a rule aimed at “payday lending” that will apply to virtually all lenders, with request for comments by Sept. 14. Here is a summary of the basic provisions of the proposed rule. However, with comments, the proposal is more than 1,300 pages in length, and the proposed rule and examples are more than 200 pages long. It is necessary to review the details of the proposed rule to understand its potential impact on your products and processes fully. You may wish to review your current and future offerings with your institution’s counsel and compliance officer to determine the potential impact if major provisions of this proposed rule are finalized by the CFPB. Coverage The proposal generally would cover two categories of loans. First, the proposal generally would cover loans with a term of 45 days or less. Second, the proposal generally would cover loans with a term greater than 45 days, provided that they have an all-in annual percentage rate greater than 36 percent and either are repaid directly from the consumer’s account or income or are secured by the consumer’s vehicle. Ability to repay For both categories of covered loans, the proposal would identify it as an abusive and unfair practice for a lender to make a covered loan without reasonably determining that the consumer has the ability to repay the loan. Or if the lender does not determine if the consumer can make payments due, as well as meet major financial obligations and basic living expenses during and for 30 days after repayment. Lenders would be required to verify the amount of income that a consumer receives, after taxes, from employment, government benefits or other sources. In addition, lenders would be required to check a consumer’s credit report to verify the amount of outstanding loans and required payments. “Safe Harbor” The proposed rule would provide lenders with options to make covered loans without satisfying the ability-to-repay and payment notice requirements, if those loans meet certain conditions. The first option would be offering loans that generally meet the parameters of the National Credit Union Administration “payday alternative loans” program, where interest rates are capped at 28 percent and the application fee is no more than $20. The other option would be offering loans that are payable in roughly equal payments with terms not to exceed two years and with an all-in cost of 36 percent or less, not including a reasonable origination fee, so long as the lender’s projected default rate on these loans is 5 percent or less. The lender would have to refund the origination fees any year that the default rate exceeds 5 percent. Lenders would be limited as to how many of either type of loan they could make per consumer per year. Outstanding loans The proposal also would impose certain restrictions on making covered loans when a consumer has — or recently had — certain outstanding loans. These provisions are extensive and differ between short- and long-term loans. For example: Payday and single-payment auto title: If a borrower seeks to roll over a loan or returns within 30 days after paying off a previous short-term debt, the lender would be restricted from offering a similar loan. Lenders could only offer a similar short-term loan if a borrower demonstrated that their financial situation during the term of the new loan would be materially improved relative to what it was since the prior loan was made. The same test would apply if the consumer sought a third loan. Even if a borrower’s finances improved enough for a lender to justify making a second and third loan, loans would be capped at three in succession followed by a mandatory 30-day cooling-off period. High-cost installment loans: For consumers struggling to make payments under either a payday installment or auto title installment loan, lenders could not refinance the loan into a loan with similar payments. This is unless a borrower demonstrated that their financial situation during the term of the new loan would be materially improved relative to what it was during the prior 30 days. The lender could offer to refinance if that would result in substantially smaller payments or would substantially lower the total cost of the consumer’s credit. Payments Furthermore, it would be defined as an unfair and abusive practice to attempt to withdraw payment from a consumer’s account for a covered loan after two consecutive payment attempts have failed, unless the lender obtains the consumer’s new and specific authorization to make further withdrawals from the account. The proposal would require lenders to provide certain notices to the consumer before attempting to withdraw payment for a covered loan from the consumer’s account unless exempt under one of the “safe harbor” options. Registered information systems Finally, the proposed rule would require lenders to use credit reporting systems to report and obtain information about loans made under the full-payment test or the principal payoff option. These systems would be considered consumer reporting companies, subject to applicable federal laws and registered with the CFPB. Lenders would be required to report basic loan information and updates to that information. The proposed regulation may be found here.

Industry’s first smart plug-and-play fraud platform allows companies to connect their own solutions, Experian products and third-party vendors in one place to better protect their customers from fraud threats Experian unveiled the fraud and identity industry’s first open platform designed to catch fraud faster, improve compliance and enhance the customer experience. Experian’s CrossCore™ gives companies an easier way to connect any new or existing tools and systems in one place, whether they are Experian, internal or third-party partner solutions. This “plug-and-play” capability allows companies to rapidly adapt to changing conditions and risks. “Our clients have expressed frustration over the lack of a truly holistic industry solution that delivers the level of confidence and control they need without requiring a massive multiyear project to replace everything they have,” said Steve Platt, global executive vice president, Fraud and Identity, Experian. “New fraud threats, updates to regulatory requirements and customer expectations for a hassle-free experience are making it challenging for fraud and compliance teams to keep up. CrossCore will give them the flexibility they need to balance customer protection with customer experience.” The CrossCore open platform enables organizations to manage services through a common access point that supports a layered approach to managing risks across providers. CrossCore includes powerful workflow and strategy design capabilities that allow fraud and compliance teams to create and adapt strategies based on evolving threats and business needs. This helps them to respond more quickly and reduces the burden on IT. Fraud and compliance teams must constantly respond to new fraud threats and changing regulatory requirements by implementing new tools on top of existing solutions. “A layered approach is imperative, because fraudsters can break through each layer individually, but they will face greater barriers with each additional layer imposed,” said Avivah Litan, vice president and distinguished analyst, Security and Privacy, of Gartner.[1] Over time, as layers have been added and fortified, systems have become increasingly complex, expensive to integrate and difficult to manage, often increasing customer friction. A key feature of the CrossCore fraud platform is the ease of integration with third-party partner solutions. At launch, CrossCore will support fraud and identity services provided by third-party partners, including Acxiom® (Identity Solutions), TeleSign and many others already integrated with Experian solutions, with more being added to the platform. Previously, integrating third-party solutions required tremendous time and effort, which often challenged in-house teams to execute in a timely, efficient manner. Through CrossCore, the responsibility of integrating additional tools and systems moves away from those teams to the platform itself, enabling clients to select best-in-class solutions from multiple providers without creating a strain on resources. Al Pascual, senior vice president, research director and head of fraud & security for Javelin, said, “There are so many great niche solutions to work with, and new ones come out almost every day. To really have a world-class approach, the client has to put all those little things together, because there never will be one vendor who does it all. The market challenge is about how to make it faster and easier to bring things together to enable a more dynamic and fluid approach to managing risk.” CrossCore features Common access through a flexible API connects disparate systems to improve risk controls while reducing integration cost and complexity An open approach enables clients to connect and optimize a portfolio of best-in-class solutions across Experian, third-party services and existing systems Powerful strategy design and workflow decisioning functions enable fraud and compliance teams to apply services in any combination to get the level of confidence required A modern Software as a Service (SaaS) architecture provides scalability and the ability to make strategy changes dynamically with no down time Experian, which offers fraud and identity services in more than 44 countries, developed CrossCore to address the widespread market need consistently expressed by its clients for a faster, easier way to get more out of their existing systems and add new tools to improve their customers’ experience while minimizing risk. Companies can begin accessing CrossCore immediately, with the ability to turn on Experian services through a single integration, connect their own fraud and identity capabilities with a common API and turn on new services as they are added. The initial release includes key Experian products: FraudNet for Account Opening; Hunter®, for application fraud detection; Prove-ID, for international identity verification; and Precise ID®, for U.S. identity verification, including knowledge-based authentication. (KBA). Third-party fraud and identity service providers can engage with CrossCore to connect their services. “Now, companies can implement a new approach to managing fraud and identity services — one that will give them greater control over their risk exposure and enable them to provide a safer and more enjoyable experience for their customers,” added Platt. Learn more about CrossCore at https://www.experian.com/crosscore [1]Gartner, Identity Proofing Revisited as Data Confidentiality Dies, Avivah Litan, Dec. 12, 2013; last reviewed on April 28, 2015

James W. Paulsen, Chief Investment Strategist for Wells Capital Management, kicked off the second day of Experian’s Vision 2016, sharing his perspective on the state of the economy and what the future holds for consumers and businesses alike. Paulsen joked this has been “the most successful, disappointing recovery we’ve ever had.” While media and lenders project fear for a coming recession, Paulsen stated it is important to note we are in the 8th year of recovery in the U.S., the third longest in U.S. history, with all signs pointing to this recovery extending for years to come. Based on his indicators – leverage, restored household strength, housing, capital spending and better global growth – there is still capacity to grow. He places recession risk at 20 to 25 percent – and only quotes those numbers due the length of the recovery thus far. “What is the fascination with crisis policies when there is no crisis,” asks Paulsen. “I think we have a good chance of being in the longest recovery in U.S. history.” Other noteworthy topics of the day: Fraud prevention Fraud prevention continues to be a hot topic at this year’s conference. Whether it’s looking at current fraud challenges, such as call-center fraud, or looking to future-proof an organization’s fraud prevention techniques, the need for flexible and innovative strategies is clear. With fraudsters being quick, and regularly ahead of the technology fighting them, the need to easily implement new tools is fundamental for you to protect your businesses and customers. More on Regulatory The Military Lending Act has been enhanced over the past year to strengthen protections for military consumers, and lenders must be ready to meet updated regulations by fall 2016. With 1.46 million active personnel in the U.S., all lenders are working to update processes and documentation associated with how they serve this audience. Alternative Data What is it? How can it be used? And most importantly, can this data predict a consumer’s credit worthiness? Experian is an advocate for getting more entities to report different types of credit data including utility payments, mobile phone data, rental payments and cable payments. Additionally, alternative data can be sourced from prepaid data, liquid assets, full file public records, DDA data, bill payment, check cashing, education data, payroll data and subscription data. Collectively, lenders desire to assess someone’s stability, ability to pay and willingness to repay. If alternative data can answer those questions, it should be considered in order to score more of the U.S. population. Financial Health The Center for Financial Services Innovation revealed insights into the state of American’s financial health. According to a study they conducted, 57 percent of Americans are not financially healthy, which equates to about 138 million people. As they continue to place more metrics around defining financial health, the center has landed on four components: how people plan, spend, save and borrow. And if you think income is a primary factor, think again. One-third of Americans making more than $60k a year are not healthy, while one-third making less than $60k a year are healthy. --- Final Vision 2016 breakouts, as well as a keynote from entertainer Jay Leno, will be delivered on Wednesday.

It’s impossible to capture all of the insights and learnings of 36 breakout sessions and several keynote addresses in one post, but let’s summarize a few of the highlights from the first day of Vision 2016. 1. Who better to speak about the state of our country, specifically some of the threats we are facing than Leon Panetta, former Secretary of Defense and Director of the CIA. While we are at a critical crossroads in the United States, there is room for optimism and his hope that we can be an America in Renaissance. 2. Alex Lintner, Experian President of Consumer Information Services, conveyed how the consumer world has evolved, in large part due to technology: 67 percent of consumers made purchases across multiple channels in the last six months. More than 88M U.S. consumers use their smartphone to do some form of banking. 68 percent of Millennials believe within five years the way we access money will be totally different. 3. Peter Renton of Lend Academy spoke on the future of Online Marketplace Lending, revealing: Banks are recognizing that this industry provides them with a great opportunity and many are partnering with Online Marketplace Lenders to enter the space. Millennials are not the largest consumers in this space today, but they will be in the future. Sustained growth will be key for this industry. The largest platforms have everything they need in place to endure – even through an economic downturn.In other words, Online Marketplace Lenders are here to stay. 4. Tom King, Experian’s Chief Information Security Officer, addressed the crowds on how the world of information security is growing increasingly complex. There are 1.9 million records compromised every day, and sadly that number is expected to rise. What can businesses do? “We need to make it easier to make the bad guys go somewhere else,” says King. 5. Look at how the housing market has changed from just a few years ago: Inventory continues to be extraordinarily lean. Why? New home building continues to run at recession levels. And, 8.5 percent of homeowners are still underwater on their mortgage, preventing them from placing it on the market. In the world of single-family home originations, 2016 projections show that there will be more purchases, less refinancing and less volume. We may see further growth in HELOC’s. With a dwindling number of mortgages benefiting from refinancing, and with rising interest rates, a HELOC may potentially be the cheapest and easiest way to tap equity. 6. As organizations balance business needs with increasing fraud threats, the important thing to remember is that the customer experience will trump everything else. Top fraud threats in 2015 included: Card Not Present (CNP) First Party Fraud/Synthetic ID Application Fraud Mobile Payment/Deposit Fraud Cross-Channel FraudSo what do the experts believe is essential to fraud prevention in the future? Big Data with smart analytics. 7. The need for Identity Relationship Management can be seen by the dichotomy of “99 percent of companies think having a clear picture of their customers is important for their business; yet only 24 percent actually think they achieve this ideal.” Connecting identities throughout the customer lifecycle is critical to bridging this gap. 8. New technologies continue to bring new challenges to fraud prevention. We’ve seen that post-EMV fraud is moving “upstream” as fraudsters: Apply for new credit cards using stolen ID’s. Provision stolen cards into mobile wallet. Gain access to accounts to make purchases.Then, fraudsters are open to use these new cards everywhere. 9. Several speakers addressed the ever-changing regulatory environment. The Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA) litigation is up 30 percent since the last year. Regulators are increasingly taking notice of Online Marketplace Lenders. It’s critical to consider regulatory requirements when building risk models and implementing business policies. 10. Hispanics and Millennials are a force to be reckoned with, so pay attention: Millennials will be 81 million strong by 2036, and Hispanics are projected to be 133 million strong by 2050. Significant factors for home purchase likelihood for both groups include VantageScore® credit score, age, student debt, credit card debt, auto loans, income, marital status and housing prices. More great insights from Vision coming your way tomorrow!

It’s one of our favorite times of year. Yes, spring is in the air, and we’re delighted to spend a few days away from the office in picturesque Scottsdale, Arizona. But what really has us excited is the opportunity to connect with a diverse network of industry leaders from across the country at our 35th annual Vision Conference. We have a full agenda, featuring sessions on advanced data analytics, market trends, fraud and identity, regulatory hot topics and more. And our theme for this year is geared toward giving participants the tools and insights they need to take control of their respective businesses to grow new markets, increase existing customer bases, reduce fraud and increase profits. In addition to 70-plus breakout session, guests will be treated to several keynote addresses: Leon Panetta, former U.S. Secretary of defense and former Director of the CIA James W. Paulsen, Chief Investment Strategist, Wells Capital Management Jay Leno, Television Host, Author and Comedian Listen to Experian North America CEO Craig Boundy’s welcome message, and start your Vision three-day event with the goal of meeting and engaging with as many old and new contacts as possible. For individuals not attending this year’s Vision, stay tuned for learnings and insights that will be shared in the coming weeks. Attendees and non-attendees alike can also follow updates on Twitter and via #vision2016.

This article first appeared in Baseline Magazine Since it is possible for cyber-criminals to create a synthetic person, businesses must be able to differentiate between synthetic and true-party identities. Children often make up imaginary friends and have a way of making them come to life. They may come over to play, go on vacation with you and have sleepover parties. As a parent, you know they don’t really exist, but you play along anyway. Think of synthetic identities like imaginary friends. Unfortunately, some criminals create imaginary identities for nefarious reasons, so the innocence associated with imaginary friends is quickly lost. Fraudsters combine and manipulate real consumer data with fictitious demographic information to create a “new” or “synthetic” individual. Once the synthetic person is “born,” fraudsters create a financial life and social history that mirrors true-party behaviors. The similarities in financial activities make it difficult to detect good from bad and real from synthetic. There really is no difference in the world of automated transaction processing between you and a synthetic identity. Often the synthetic “person” is viewed as a thin or shallow file consumer— perhaps a millennial. I have a hard time remembering all of my own passwords, so how do organized “synthetic schemes” keep all the information usable and together across hundreds of accounts? Our data scientists have found that information is often shared from identity to identity and account to account. For instance, perhaps synthetic criminals are using the same or similar passwords or email addresses across products and accounts in your portfolio. Or, perhaps physical address and phone records have cross-functional similarities. The algorithms and sciences are much more complex, but this simplifies how we are able to link data, analytics, strategies and scores. Identifying the Business Impact of Synthetic-Identity Fraud Most industry professionals look at synthetic-identity fraud as a relatively new fraud threat. The real risk runs much deeper in an organization than just operational expense and fraud loss dollars. Does your fraud strategy include looking at all types of risk, compliance reporting, and how processes affect the customer experience? To identify the overall impact synthetic identities can have on your institution, you should start asking: Are you truly complying with "Know Your Customer" (KYC) regulations when a synthetic account exists in your active portfolio? Does your written "Customer Identification Program" (CIP) include or exclude synthetic identities? Should you be reporting this suspicious activity to the compliance officer (or department) and submitting a suspicious activity report (SAR)? Should you charge off synthetic accounts as credit or fraud losses? Which department should be the owner of suspected synthetic accounts: Credit Risk, Collections or Fraud? Do you have run any anti-money laundering (AML) risk when participating in money movements and transfers? Depending on your answers to the above questions, you may be incurring potential risks in the policies and procedures of synthetic identity treatment, operational readiness and training practices. Since it is possible to create a synthetic person, businesses must be able to differentiate between synthetic and true-party identities, just as parents need to differentiate between their child's real and imaginary friends.

Businesses are looking to international markets to fuel growth, but meeting regulatory requirements across the globe poses significant challenges. Changes in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements are evolving at break-neck speed. In the past few years, financial institutions and corporations have incurred billions of dollars in fines, reputation damage, and even the possibility of criminal prosecution for not enforcing adequate regulatory controls. KPMG found that 70 percent of its respondents had received a regulatory visit within the past year focused on KYC and total investment in AML had increased by an average rate of 53 percent. As large as this additional investment may seem, there may be an even bigger cost to doing regulatory compliance the right way. For many businesses the customer experience is the biggest casualty of implementing a robust KYC program. In their Vision 2016 breakout session “Know your customer, meeting commercial requirements in a global marketplace,” Greg Carmean, Experian senior product manager, will be joined by Adel Shrufi, software development manager at Amazon Transaction Risk Management Systems. They will discuss: • How to streamline compliance to optimize the client experience • How to evaluate and select the best vendors to reduce compliance costs and operational vulnerabilities • What businesses need to consider to ensure successful launches in new international markets Watch our session preview video below: We’ll look forward to seeing you as we provide a road map for growth at this year’s Vision conference.

Device emulators — wolves in sheep’s clothing Despite all the fraud prevention systems and resources in the public and private sectors, online fraud continues to grow at an alarming rate, offering a low-risk, high-reward proposition for fraudsters. Unfortunately, the Web houses a number of easily accessible tools that criminals can use to perpetrate fraud and avoid detection. The device emulator is one of these tools. Simply put, a device emulator is one device that pretends to be another. What began as innovative technology to enable easy site testing for Web developers quickly evolved into a universally available tool that attackers can exploit to wreak havoc across all industry verticals. While it’s not new technology, there has been a significant increase in its use by criminals to deceive simple device identification and automated risk-management solutions to carry out fraudulent activities. Suspected device emulation (or spoofing) traffic historically has been difficult to identify because fraud solutions rely heavily on reputation databases or negative lists. Detecting and defeating these criminals in sheep’s clothing is possible, however. Leveraging Experian’s collective fraud intelligence and data modeling expertise, our fraud research team has isolated several device attributes that can identify the presence of an emulator being used to submit multiple transactions. Thanks to these latest FraudNet rule sets, financial institutions, ecommerce merchants, airlines, insurers and government entities alike now can uncloak and protect against many of these cybercriminals. Unfortunately, device emulators are just one of many tools available to criminals on the Dark Web. Join me at Vision 2016, where U.S. Secret Service and I will share more tales from the Dark Web. We will explore the scale of the global cybercrime problem, walk through the anatomy of a typical hack, explain how hackers exploit browser plug-ins, and describe how enhanced device intelligence and visibility across all channels can stop fraudsters in their tracks. Listen to Mike Gross as he shares a short overview of his Vision 2016 breakout session in this short video. Don’t miss this innovative Vision 2016 session! See you there.
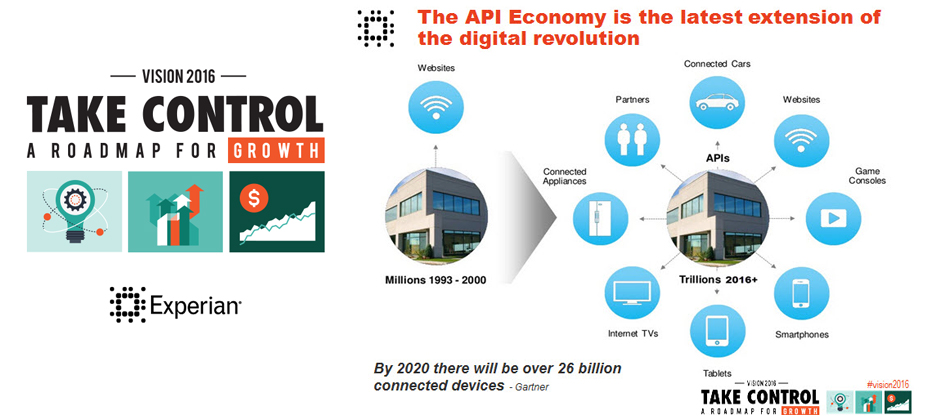
There is a revolution going on! We are in the midst of the second phase of the digital revolution and it is being fueled by API’s. API’s provide the access and mapping that allow access to and integration of the myriad of existing and new data sources available today. They do really helpful things like allow Uber to revolutionize the connection of riders to drivers as well as allow for quick, self-service credit decisions by integrating Experian data within Salesforce.com. Digital disruptors like Uber have scaled their business to massive size at breakneck speed because they can design, build and deploy solutions quickly. API’s and cloud computing play a central role in all of this. You will hear representatives from Uber share how API’s enabled the flow of Experian data through Salesforce.com enabling them to launch new business models, and enter new markets. Listen to Mike Myers as he shares a short overview of his Vision 2016 breakout session in this short video. Don’t miss this innovative Vision 2016 session! See you there.

Small business trade payment delinquencies can signal the beginning of business financial duress. However, sometimes these delinquencies are isolated events. Understanding the trade payment priorities of a business can lead to better business risk assessment. Experian understands commercial payment behaviors and can help clients more accurately interpret the risk of payment delinquencies for different kinds of trades. In his Vision 2016 breakout session “Which creditors get priority when businesses face a financial burden”, Sung Park, Analytics Consultant with Experian’s Decision Sciences discusses the types of trades or financial obligations that become delinquent first, and the conditions that most commonly signal overall business stress. What the audience will learn: The audience will have a better understanding of which type of trade delinquencies are likely isolated incidents and which ones are precursors of businesses facing a financial burden, and what actions can be taken proactively to mitigate risk. Don't miss your opportunity to catch these informative breakout sessions during Vision 2016.

Identity management traditionally has been made up of creating rigid verification processes that are applied to any access scenario. But the market is evolving and requiring an enhanced Identity Relationship Management strategy and framework. Simply knowing who a person is at one point in time is not enough. The need exists to identify risks associated with the entire identity profile, including devices, and the context in which consumers interact with businesses, as well as to manage those risks throughout the consumer journey. The reasoning for this evolution in identity management is threefold: size and scope, flexible credentialing and adaptable verification. First, deploying a heavy identity and credentialing process across all access scenarios is unnecessarily costly for an organization. While stringent verification is necessary to protect highly sensitive information, it may not be cost-effective to protect less-valuable data with the same means. A user shouldn’t have to go through an extensive and, in some cases, invasive form of identity verification just to access basic information. Second, high-friction verification processes can impede users from accessing services. Consumers do not want to consistently answer multiple, intrusive questions in order to access basic information. Similarly, asking for personal information that already may have been compromised elsewhere limits the effectiveness of the process and the perceived strength in the protection. Finally, an inflexible verification process for all users will detract from a successful customer relationship. It is imperative to evolve your security interactions as confidence and routines are built. Otherwise, you risk severing trust and making your organization appear detached from consumer needs and preferences. This can be used across all types of organizations — from government agencies and online retailers to financial institutions. Identity Relationship Management has three unique functions delivered across the Customer Life Cycle: Identity proofing Authentication Identity management Join me at Vision 2016 for a deeper analysis of Identity Relationship Management and how clients can benefit from these new capabilities to manage risk throughout the Customer Life Cycle. I look forward to seeing you there!