What Is Cybersecurity?
Quick Answer
Cybersecurity broadly refers to all the hardware, software and practices that you can use to keep your devices and data safe. There’s no foolproof method to stay safe; however, keeping your software up to date, using account protection features and learning how to spot attackers can help protect you from common threats.

The importance of cybersecurity is increasing as cyberattacks become more prevalent and the damage they cause increases. Whether you manage finances online, have social media profiles or want to keep your personal information private, implementing a few cybersecurity best practices can help.
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the wide range of processes and tools that people, businesses and governments use to keep their networks, devices and information safe.
Although technology is important for cybersecurity, good cyber hygiene doesn't depend entirely on technology. For example, keeping your devices updated and using antivirus software is helpful. But the human factor, such as knowing to avoid clicking on links in unexpected emails, can be just as important.
Why Is Cybersecurity Important?
Cybersecurity is important for individuals because attackers can do a lot of harm if they gain access to your devices. For example, cybersecurity can help you:
- Reduce the likelihood of identity theft: Attackers may be able to steal your personal information, including your name, address, Social Security number and other sensitive information. They might use it to steal your identity or sell your information to other criminals.
- Stop different types of fraud: Attackers also might be able to use your stolen information or access to your devices to commit different types of fraud, including opening credit accounts in your name or taking over your accounts.
- Avoid hurting others: Rather than going after you directly, the attackers might commandeer your machine to help them launch other types of cyberattacks. Your device could be under the criminal's control without showing any signs of a change.
Cybersecurity is also important for businesses and governments, which often have more to lose. For example, a data breach could expose millions of people's personal information, or a ransomware attack might take critical infrastructure offline, such as a hospital or pipeline.
Different Types of Cybersecurity Threats
There are many types of cybersecurity threats, including complex attacks that are government-funded and coordinated. But most individuals don't need to worry about these cyber threats. Instead, focus on the more common threats listed below.
| Threat Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Malware | Malicious software designed to harm or exploit systems | Spyware, ransomware, viruses, worms, trojans |
| Phishing | Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information via fake emails, texts or phone calls | Email scams, fake login pages |
| Smishing | Fake text messages to trick victims into clicking malicious links or giving up sensitive information | Bank impersonation, fake prize, gift or delivery texts |
| Ransomware | Malware that encrypts data and demands payment for decryption | Encryptors, lockers, leakware, scareware |
| Social engineering | Techniques that scammers use to gain your trust and trick you into revealing confidential information | Pretexting, baiting |
| Credential stuffing | When scammers use stolen credentials to gain unauthorized access to different websites | Automated login attempts |
| Spoofing | When a scammer makes it look like an email or text is coming from someone else | Email, caller ID and website spoofing |
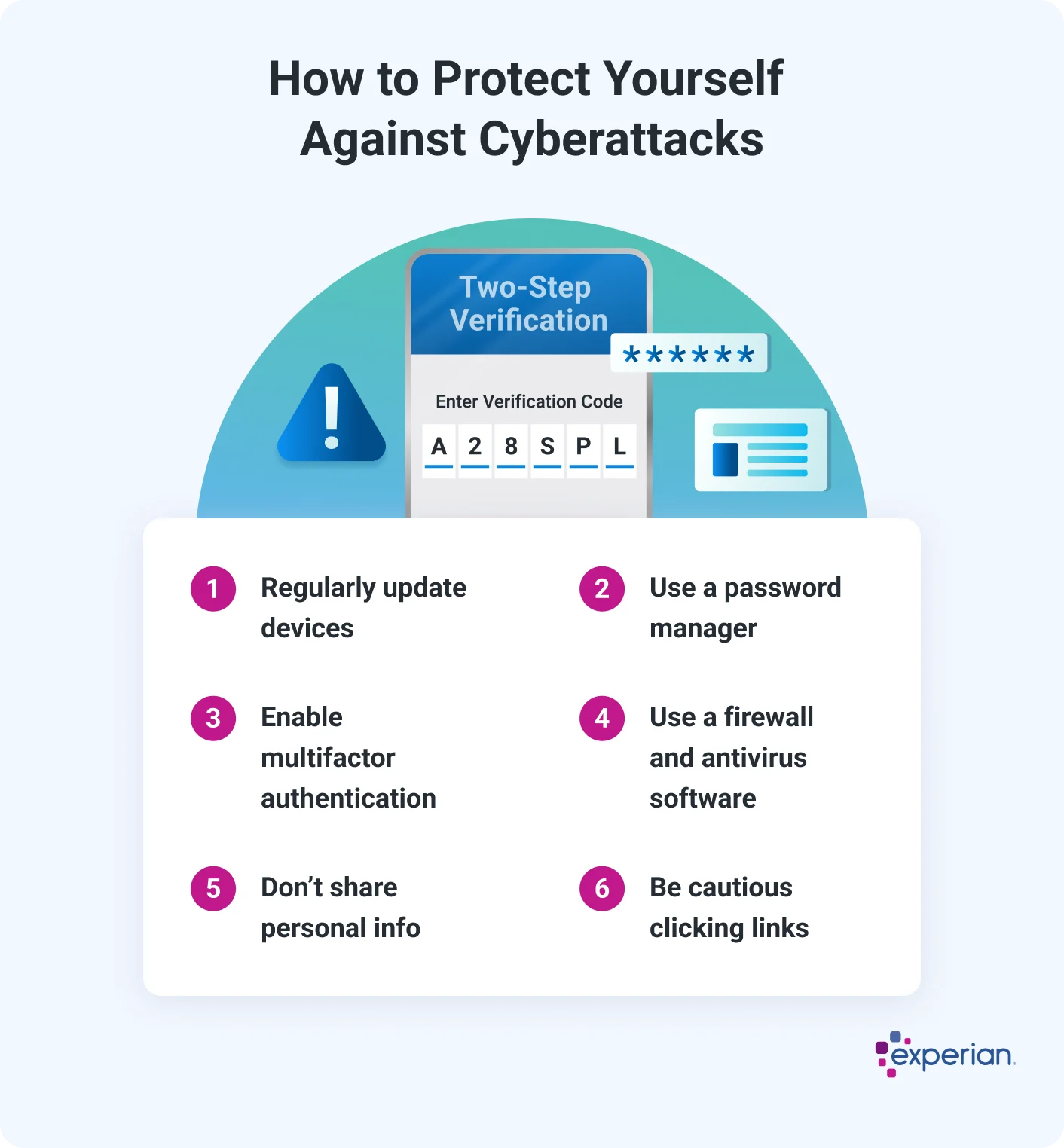
How to Protect Yourself Against Cyberattacks
There's no foolproof way to protect yourself from every type of cyberattack. There's even a name for cyberattacks that don't have known defenses—zero-day attacks, because there have been zero days to fix the issue that makes the attack possible.
However, there are well-known and relatively easy tools and practices that you can use to help protect yourself from common attacks.
- Regularly update devices. Updating the software on your phone, computer and other devices can patch newly discovered vulnerabilities. You can look for options to automatically install updates at convenient times, such as the middle of the night.
- Use a password manager. Creating strong and unique passwords that you can remember for all your online accounts is practically impossible on your own. But a password manager can help you generate, securely store and fill in passwords.
- Enable multifactor authentication. Multifactor authentication (MFA) requires someone to use at least two forms of identification to access a device or account, such as a username and password, plus a code sent to your email. Turning on MFA when available can help stop someone from accessing or taking over your account.
- Use a firewall and antivirus software. Many devices come with firewalls and antivirus protections built in—keep these turned on and up to date. Additional free or paid antivirus programs might offer extra protections or features.
- Don't share your personal information. Criminals might use personal information that you post online to threaten you, imitate you or break into your accounts.
- Beware of links and attachments. Learn how to spot a spoofed email and always be suspicious of emails and text messages that ask you to share personal information or click on a link. Often, the sender will pretend to be from a government agency or well-known company.
Next Steps for Staying Safe
Putting defenses into place and staying vigilant can help protect you from cyberattacks. Additionally, you can:
- See if your personal information was compromised. Use Experian's free dark web scan and check HaveIBeenPwned to find out if your email, phone number and other information was compromised in a data breach or if it's available on the dark web.
- Find out what personal information is on the open web. Your personal information might be widely available online. Try Experian's personal privacy scan to get a free scan and find out what's on people finder websites.
- Look into identity theft protection. Although cyber attacks don't always lead to identity theft, you may also want to consider an identity theft protection service. Some of these services, such as Experian IdentityWorks℠, come with ongoing monitoring, identity theft insurance and access to fraud resolution specialists.
While cybersecurity comes in many forms, taking protective measures on your own is an important first step in safeguarding your information.
Is your info on the dark web?
Internet criminals buy and sell personal data on the dark web to commit fraud. Could they have your info? Find out with a free Dark Web Scan.
Run a free scanAbout the author
Louis DeNicola is freelance personal finance and credit writer who works with Fortune 500 financial services firms, FinTech startups, and non-profits to teach people about money and credit. His clients include BlueVine, Discover, LendingTree, Money Management International, U.S News and Wirecutter.
Read more from Louis